| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Easy |
|
You are given the root of a binary search tree (BST) and an integer val.
Find the node in the BST that the node's value equals val and return the subtree rooted with that node. If such a node does not exist, return null.
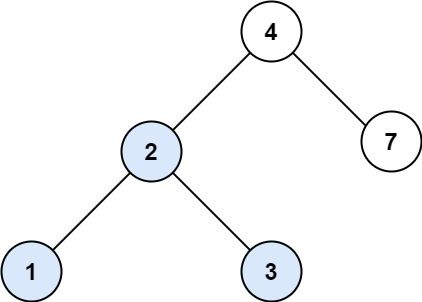
Example 1:
Input: root = [4,2,7,1,3], val = 2 Output: [2,1,3]
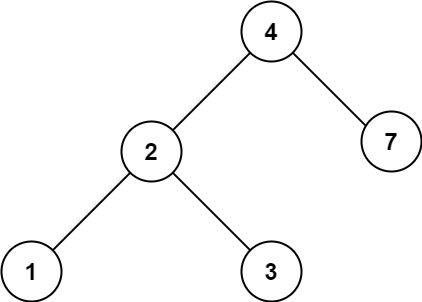
Example 2:
Input: root = [4,2,7,1,3], val = 5 Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 5000]. 1 <= Node.val <= 107rootis a binary search tree.1 <= val <= 107
We check if the current node is null or if the current node's value equals the target value. If so, we return the current node.
Otherwise, if the current node's value is greater than the target value, we recursively search the left subtree; otherwise, we recursively search the right subtree.
The time complexity is
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def searchBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], val: int) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if root is None or root.val == val:
return root
return (
self.searchBST(root.left, val)
if root.val > val
else self.searchBST(root.right, val)
)/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if (root == null || root.val == val) {
return root;
}
return root.val > val ? searchBST(root.left, val) : searchBST(root.right, val);
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* searchBST(TreeNode* root, int val) {
if (!root || root->val == val) {
return root;
}
return root->val > val ? searchBST(root->left, val) : searchBST(root->right, val);
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func searchBST(root *TreeNode, val int) *TreeNode {
if root == nil || root.Val == val {
return root
}
if root.Val > val {
return searchBST(root.Left, val)
}
return searchBST(root.Right, val)
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function searchBST(root: TreeNode | null, val: number): TreeNode | null {
if (root === null || root.val === val) {
return root;
}
return root.val > val ? searchBST(root.left, val) : searchBST(root.right, val);
}