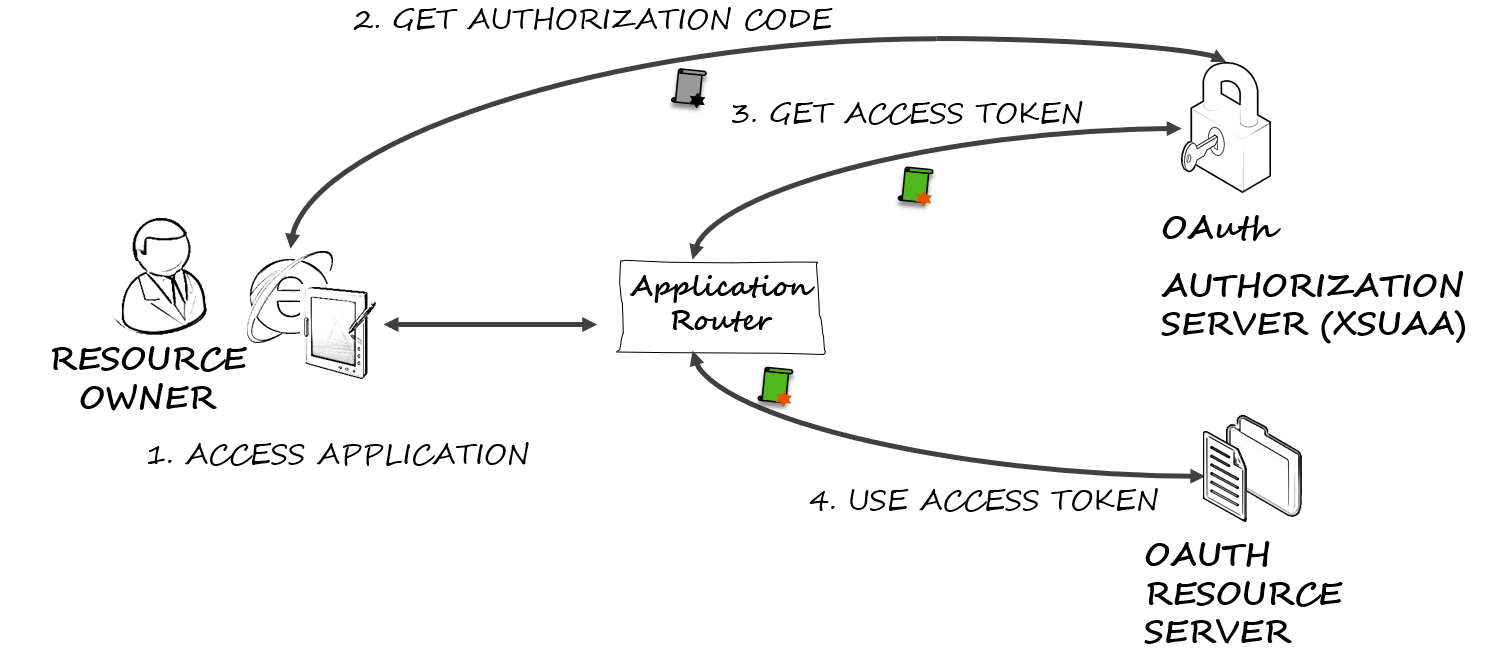
This project is a python client library called sap-xssec for validation of OAuth access tokens issued by the XSUAA.
The typical web application use the OAuth authorization code flow for authentication, which is described as follows:
- A user accesses the web application using a browser.
- The web application (in typical SAP Cloud Platform applications, this is an application router) acts as OAuth client and redirects to the OAuth server for authorization.
- Upon authentication, the web application uses the code issued by the authorization server to request an access token.
- The web application uses the access token to request data from the OAuth resource server. The OAuth resource server validates the token using online or offline validation. For this validation libraries like sap-xssec are used.
For the usage of this library it is necessary to pass a JWT access token that should be validated to the library. The examples below rely on users and credentials that you should substitute with the ones in your context.
The typical use case for calling this API lies from within a container when an HTTP request is received and it must
be checked if the requester is authorized to execute this method.
In this case, the access token is contained in the authorization header (with keyword bearer).
You can remove the prefix bearer and pass the remaining string (just as in the following example as access_token) to the API.
from sap import xssec
from cfenv import AppEnv
env = AppEnv()
uaa_service = env.get_service(name='<uaa_service_name>').credentials
security_context = xssec.create_security_context(access_token, uaa_service)Note: That the example above uses module cfenv to retrieve the configuration of the uaa
service instance.
uaa_service is a dict that contains the necessary client information and looks like:
{
'clientid' : 'example_clientid' // the id of the client
'clientsecret': 'example_clientsecret' // the secret of the client
'url': 'example_url' // the url of the uaa
'uaadomain': 'example_uaadomain' // the domain of the uaa
'verificationkey': 'example_verification key' // (optional) the key used for the verfication of the token
}
If the uaadomain is set in the uaa_service and the jku and kid are set in the incomming token, the key is requested from the uaa. As a fallback, the verificationkey configured in uaa_service is used for offline validation. Requested keys are cached for 15 minutes to avoid extensive load on the uaa.
The creation function xssec.create_security_context is to be used for an end-user token (e.g. for grant_type password
or grant_type authorization_code) where user information is expected to be available within the token and thus within the security context.
create_security_context also accepts a token of grant_type client_credentials.
This leads to the creation of a limited SecurityContext where certain functions are not available.
For more details please consult the API description in the wiki.
For example, the security_context object can then be used to check if a user has a required scope:
security_context.check_scope('uaa.user')
or to receive the client id of a user:
security_context.get_clientid()
More details on the API can be found in the wiki.
sap-xssec offers offline validation of the access token, which requires no additional call to the UAA.
The trust for this offline validation is created by binding the XS UAA service instance to your application.
Inside the credentials section in the environment variable VCAP_SERVICES, the key for validation of tokens is included.
By default, the offline validation check will only accept tokens intended for the same OAuth2 client in the same UAA identity zone.
This makes sense and will cover the vast majority of use cases.
SAP_JWT_TRUST_ACL environment variable is no longer supported.
If you want to enable another (foreign) application to use some of your application's scopes, you can add a granted-apps marker to your scope in the xs-security.json file (as in the following example). The value of the marker is a list of applications that is allowed to request a token with the denoted scope.
{
"xsappname" : "sample-leave-request-app",
"description" : "This sample application demos leave requests",
"scopes" : [ { "name" : "$XSAPPNAME.createLR",
"description" : "create leave requests" },
{ "name" : "$XSAPPNAME.approveLR",
"description" : "approve leave requests",
"granted-apps" : ["MobileApprovals"] }
],
"attributes" : [ { "name" : "costcenter",
"description" : "costcenter",
"valueType" : "string"
} ],
"role-templates": [ { "name" : "employee",
"description" : "Role for creating leave requests",
"scope-references" : [ "$XSAPPNAME.createLR","JobScheduler.scheduleJobs" ],
"attribute-references": [ "costcenter"] },
{ "name" : "manager",
"description" : "Role for creating and approving leave requests",
"scope-references" : [ "$XSAPPNAME.createLR","$XSAPPNAME.approveLR","JobScheduler.scheduleJobs" ],
"attribute-references": [ "costcenter" ] }
]
}To configure whether the sap-jwt or the py-jwt library should be used for validation of the jwt token,
change the USE_SAP_PY_JWT environment variable to true.
USE_SAP_PY_JWT environment variable is no longer supported and therefore py-jwt is installed by default.
sap-xssec requires python 3.7 or newer.
As this package is deployed to PyPI, you can simply add sap-xssec as a dependency to your python project or
install this package by running pip install sap-xssec.
Open an issue in GitHub.