Application to comfortably monitor your Internet traffic
Cross-platform, Intuitive, Reliable
Translated in:
🇨🇳 🇩🇪 🇫🇷 🇷🇺 🇵🇹 🇪🇦 🇮🇹 🇵🇱 + 12 more languages


Sniffnet is completely free, open-source software which needs lots of effort and time to develop and maintain.
If you appreciate Sniffnet, consider sponsoring: your support will allow me to dedicate more time to this project, constantly expanding it including new features and functionalities.
A special mention goes to these awesome organizations and folks who are sponsoring Sniffnet:
| 64‑bit | 32‑bit | Intel | Apple silicon | amd64 | arm64 | i386 | armhf | x86_64 | aarch64 |
Links in the table above will download the latest version of Sniffnet directly from GitHub releases.
Note
Remember to also install the required dependencies for your operating system.
Alternative installation methods are reported in the following:
from Crates.io
Follow this method only if you have Rust installed on your machine.
In this case, the application binary can be built and installed with:
cargo install sniffnet --lockedfrom Nixpkgs
You can install Sniffnet Nix package adding the following Nix code to your NixOS Configuration, usually located in /etc/nixos/configuration.nix:
environment.systemPackages = [
pkgs.sniffnet
];Alternatively, you can install it in your home using Home Manager with:
home.packages = [
pkgs.sniffnet
];Alternatively, you can try it in a shell with:
nix-shell -p sniffneton FreeBSD
You can install Sniffnet port with:
pkg install sniffneton Tiny Core Linux
You can install Sniffnet from the official repository with:
tce-load -wi sniffnet
- 💻 choose a network adapter of your PC to inspect
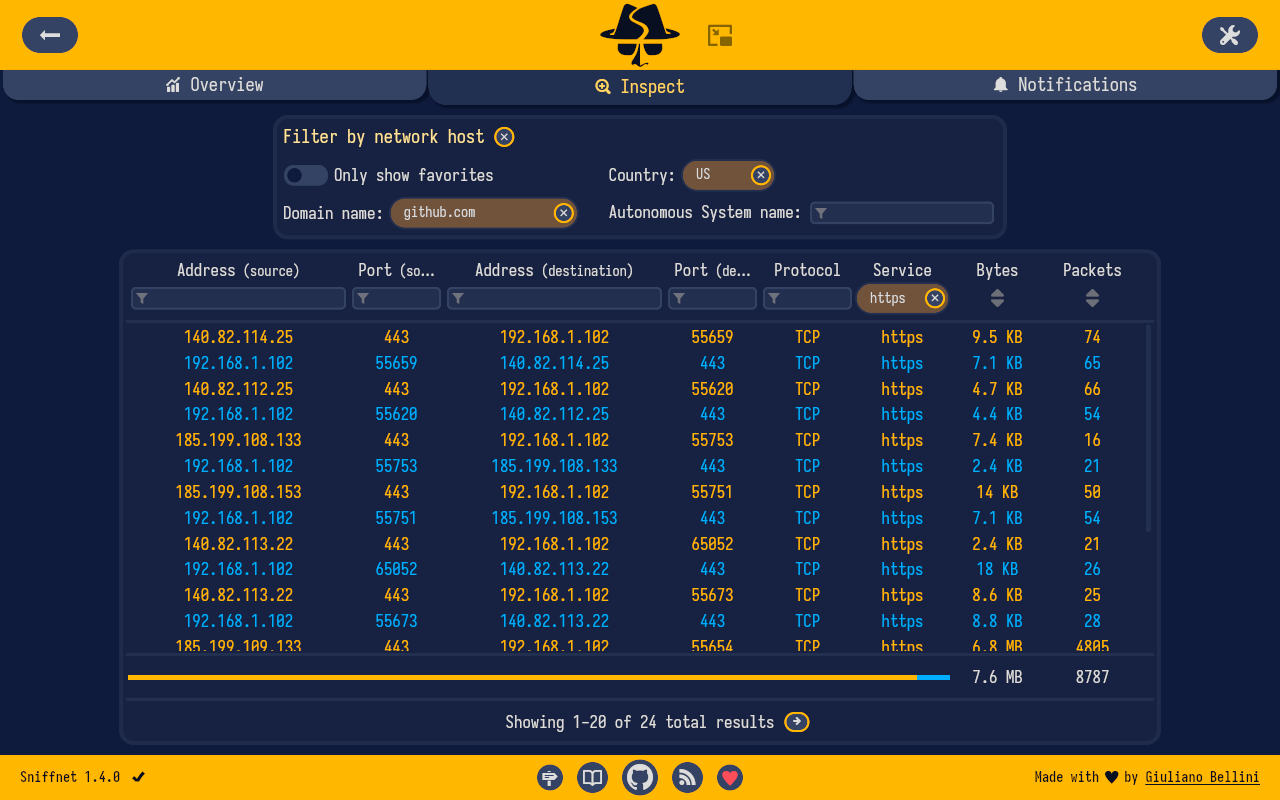
- 🏷️ select a set of filters to apply to the observed traffic
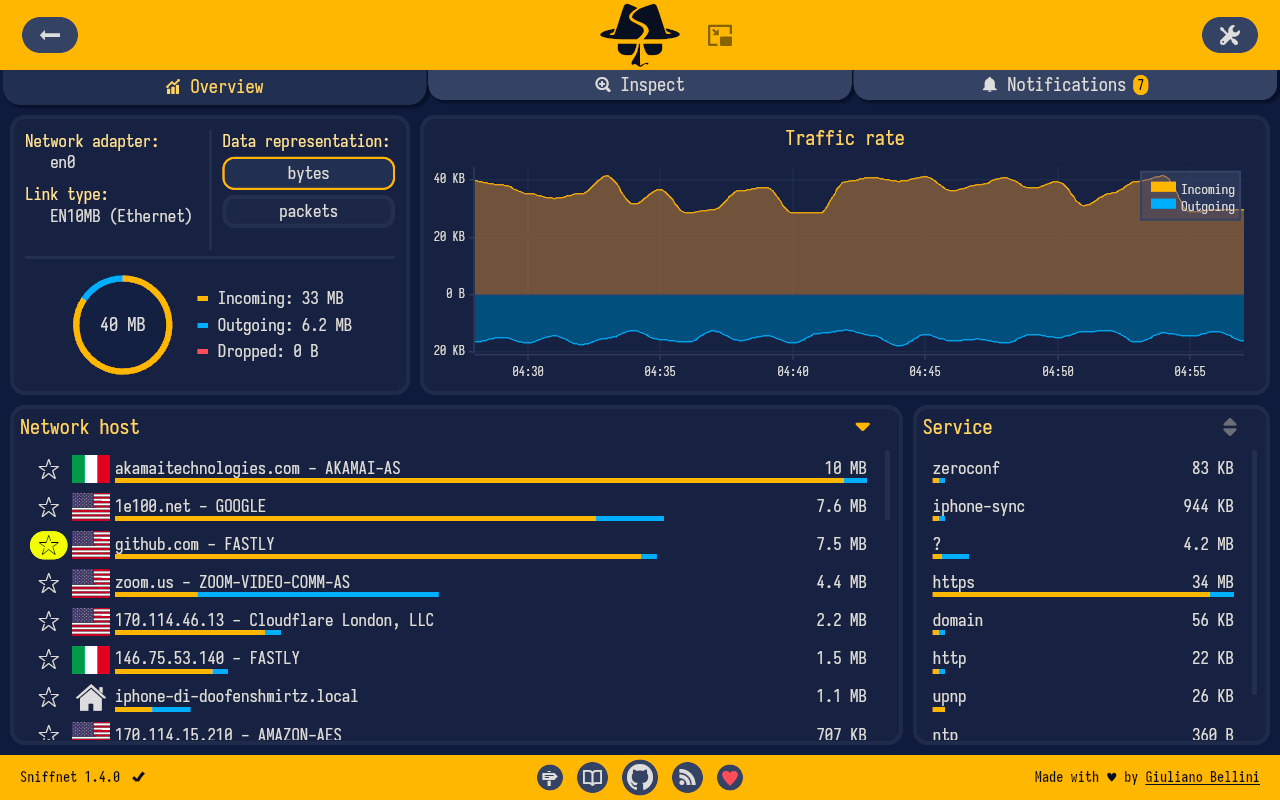
- 📖 view overall statistics about your Internet traffic
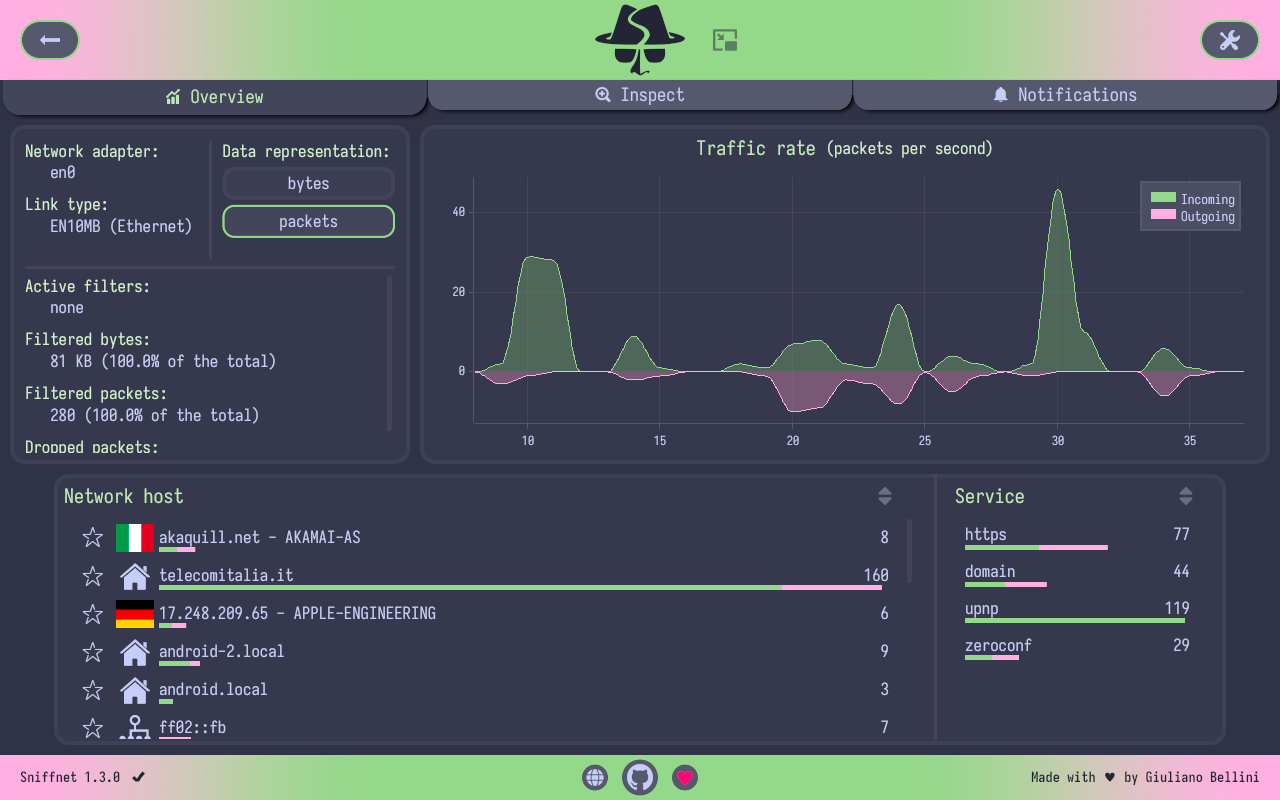
- 📈 view real-time charts about traffic intensity
- 📌 keep an eye on your network even when the application is minimized
- 📁 export comprehensive capture reports as PCAP files
- 🔎 identify 6000+ upper layer services, protocols, trojans, and worms
- 🌐 find out domain name and ASN of the hosts you are exchanging traffic with
- 🏠 identify connections in your local network
- 🌍 get information about the country of remote hosts (IP geolocation)
- ⭐ save your favorite network hosts
- 🕵️♂️ search and inspect each of your network connections in real time
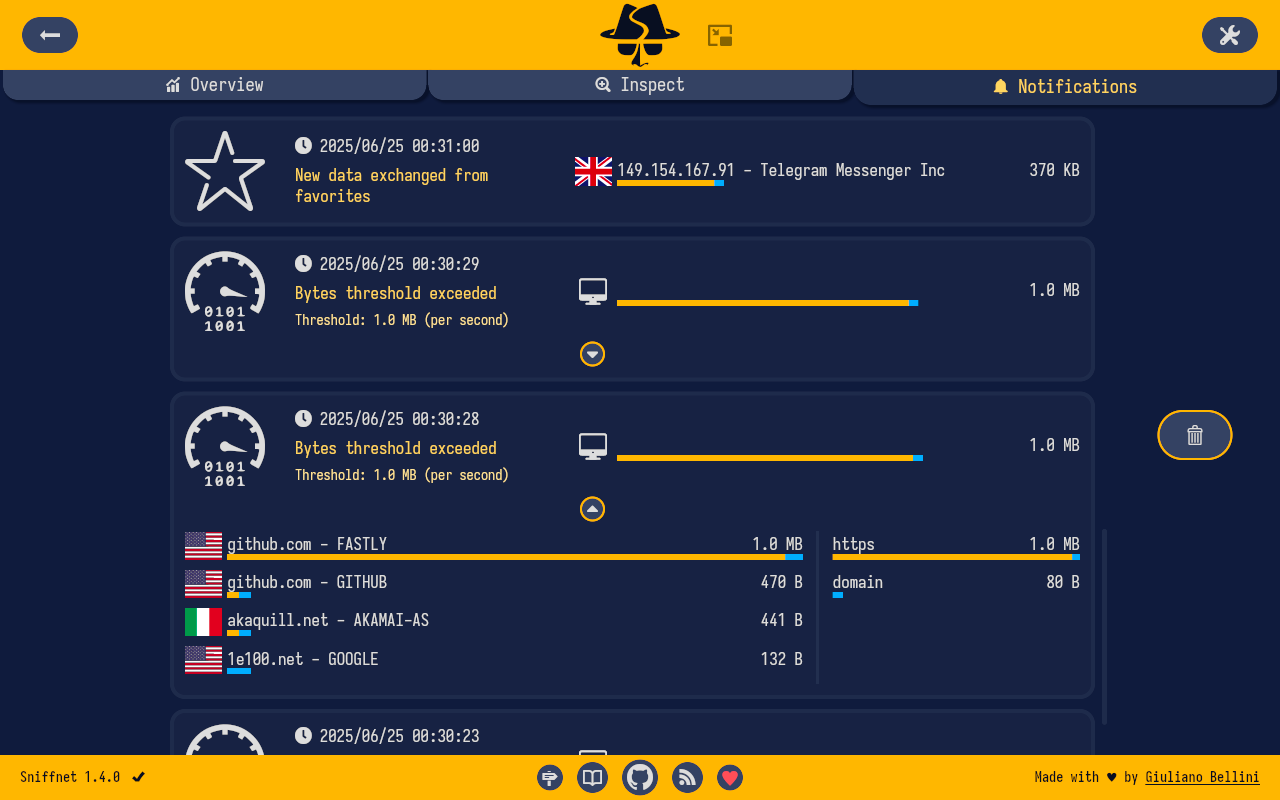
- 🔉 set custom notifications to inform you when defined network events occur
- 🎨 choose the style that fits you the most, including custom themes support
- ...and more!
Do you want to learn more?
Check out the Sniffnet Wiki, a comprehensive manual to help you
thoroughly master the application from a basic setup to the most advanced functionalities.
The Wiki includes step-by-step guides, tips, examples of usage, and answers to frequent questions.
See details
Most of the errors that may arise are likely due to your system missing dependencies
required to correctly analyze a network adapter.
Check the required dependencies page
for instructions on how to proceed depending on your operating system.
In some circumstances, especially if you are running on an old architecture or your graphical drivers are not updated,
the wgpu default renderer used by iced
may manifest bugs (the interface glitches, color gradients are unsupported, or some icons are completely black).
In these cases you can set an environment variable to switch to the tiny-skia renderer,
a CPU-only software renderer that should work properly on every environment:
ICED_BACKEND=tiny-skiaIn any case, don't hesitate to open an issue, and I will do my best to help you!
- A big shout-out to all the contributors of Sniffnet!
- The graphical user interface has been realized with iced, a cross-platform GUI library for Rust focused on simplicity and type-safety
- IP geolocation and ASN data are provided by MaxMind
- Last but not least, thanks to every single stargazer: all forms of support made it possible to keep improving Sniffnet!