-
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 1.9k
Attributes
Note attributes are key-value records owned by (assigned to) given note.
There are four types of attributes:
- Labels - simple key-value text record
- Relation - specifies named relation (link) to another note
- Label and relation definition - these are described in Promoted attributes page
Sometimes we're talking about labels and relations - keep in mind that both of them are types of attributes.
Labels are used for several things:
- user can use them as labels with optional value - e.g. when catalogizing books, you might add labels like @year=1999, @genre=sci-fi, @author="Neal Stephenson"
- attributes can be used to configure some advanced features / settings - see below
- plugins / scripts can use these to mark notes with some special values / metadata (e.g. Weight Tracker will have "weight" attribute on day notes based on whose it can create chart).
Labels can be used for searching.
Following labels are used for advanced configuration:
-
disableVersioning- disables auto-versioning. Useful for e.g. large, but unimportant notes - e.g. large JS libraries used for scripting -
calendarRoot- marks note which should be used as root for day notes. Only one should be marked as such. -
archived- notes with this label won't be visible in autocomplete-based search (jump to, add link). Applies also to all its sub-notes. -
excludeFromExport- notes (with their sub-tree) won't be included in any note export -
run- defines on which events script should run. Possible values are:-
frontendStartup- when Trilium frontend starts up (or is refreshed). -
backendStartup- when Trilium backend starts up -
hourly- run once an hour -
daily- run once a day
-
-
disableInclusion- scripts with this label won't be included into parent script execution. -
sorted- keeps child notes sorted by title alphabetically hidePromotedAttributes-
readOnly- editor is in read only mode. Works only for text notes. See some use cases here. -
autoReadOnlyDisabled- text/code notes can be set automatically into read mode when they are too large. You can disable this behavior on per-note basis by adding this label to the note -
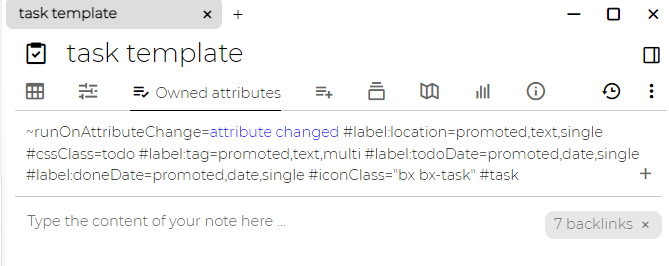
cssClass- value of this label is then added as CSS class to the node representing given note in the tree. This can be useful for advanced theming. Can be used intemplatenotes. -
iconClass- value of this label is added as a CSS class to the icon on the tree which can help visually distinguish the notes in the tree. Example might bebx bx-home- icons are taken from boxicons. Can be used in template notes. -
customRequestHandlerandcustomResourceProvider- see Custom request handler
Relation is a kind of link between two notes.
This could be used when you e.g. keep a book database, you can use relations to keep formal links between the book (note) and the book's author (note) by defining an "author" relation on the book note pointing to the author's note.
Relations are used also for some advanced scripting - like attaching scripts to events happening on certain note.
-
runOnNoteCreation- executes when note is created on backend -
runOnNoteTitleChange- executes when note title is changed (includes note creation as well) -
runOnNoteChange- executes when note is changed (includes note creation as well) -
runOnChildNoteCreation- executes when new note is created under this note -
runOnAttributeCreation- executes when new attribute is created under this note -
runOnAttributeChange- executes when attribute is changed under this note
Other relations:
-
template- attached note's attributes will be inherited even without parent-child relationship. See template for details. -
renderNote- notes of type "render HTML note" will be rendered using a code note (HTML or script) and it is necessary to point using this relation to which note should be rendered -
widget- target of this relation will be executed and rendered as a widget in the sidebar
Attributes allow multiplicity - there can be multiple attributes with the same name. We're then calling such attributes "multi valued".
Back to Overview
- Screenshot tour
- Basic concepts
- Installation & setup
- Advanced usage
- Developer guides
- FAQ
- Troubleshooting