| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
1710 |
Weekly Contest 418 Q2 |
|
You are maintaining a project that has n methods numbered from 0 to n - 1.
You are given two integers n and k, and a 2D integer array invocations, where invocations[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that method ai invokes method bi.
There is a known bug in method k. Method k, along with any method invoked by it, either directly or indirectly, are considered suspicious and we aim to remove them.
A group of methods can only be removed if no method outside the group invokes any methods within it.
Return an array containing all the remaining methods after removing all the suspicious methods. You may return the answer in any order. If it is not possible to remove all the suspicious methods, none should be removed.
Example 1:
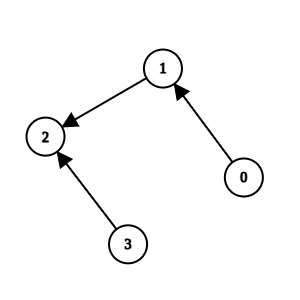
Input: n = 4, k = 1, invocations = [[1,2],[0,1],[3,2]]
Output: [0,1,2,3]
Explanation:
Method 2 and method 1 are suspicious, but they are directly invoked by methods 3 and 0, which are not suspicious. We return all elements without removing anything.
Example 2:
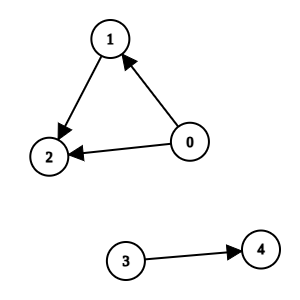
Input: n = 5, k = 0, invocations = [[1,2],[0,2],[0,1],[3,4]]
Output: [3,4]
Explanation:
Methods 0, 1, and 2 are suspicious and they are not directly invoked by any other method. We can remove them.
Example 3:
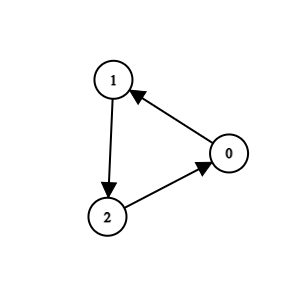
Input: n = 3, k = 2, invocations = [[1,2],[0,1],[2,0]]
Output: []
Explanation:
All methods are suspicious. We can remove them.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 1050 <= k <= n - 10 <= invocations.length <= 2 * 105invocations[i] == [ai, bi]0 <= ai, bi <= n - 1ai != biinvocations[i] != invocations[j]
We can start from
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def remainingMethods(
self, n: int, k: int, invocations: List[List[int]]
) -> List[int]:
def dfs(i: int):
suspicious[i] = True
for j in g[i]:
if not suspicious[j]:
dfs(j)
def dfs2(i: int):
vis[i] = True
for j in f[i]:
if not vis[j]:
suspicious[j] = False
dfs2(j)
f = [[] for _ in range(n)]
g = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for a, b in invocations:
f[a].append(b)
f[b].append(a)
g[a].append(b)
suspicious = [False] * n
dfs(k)
vis = [False] * n
ans = []
for i in range(n):
if not suspicious[i] and not vis[i]:
dfs2(i)
return [i for i in range(n) if not suspicious[i]]class Solution {
private boolean[] suspicious;
private boolean[] vis;
private List<Integer>[] f;
private List<Integer>[] g;
public List<Integer> remainingMethods(int n, int k, int[][] invocations) {
suspicious = new boolean[n];
vis = new boolean[n];
f = new List[n];
g = new List[n];
Arrays.setAll(f, i -> new ArrayList<>());
Arrays.setAll(g, i -> new ArrayList<>());
for (var e : invocations) {
int a = e[0], b = e[1];
f[a].add(b);
f[b].add(a);
g[a].add(b);
}
dfs(k);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (!suspicious[i] && !vis[i]) {
dfs2(i);
}
}
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (!suspicious[i]) {
ans.add(i);
}
}
return ans;
}
private void dfs(int i) {
suspicious[i] = true;
for (int j : g[i]) {
if (!suspicious[j]) {
dfs(j);
}
}
}
private void dfs2(int i) {
vis[i] = true;
for (int j : f[i]) {
if (!vis[j]) {
suspicious[j] = false;
dfs2(j);
}
}
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<int> remainingMethods(int n, int k, vector<vector<int>>& invocations) {
vector<bool> suspicious(n);
vector<bool> vis(n);
vector<int> f[n];
vector<int> g[n];
for (const auto& e : invocations) {
int a = e[0], b = e[1];
f[a].push_back(b);
f[b].push_back(a);
g[a].push_back(b);
}
auto dfs = [&](this auto&& dfs, int i) -> void {
suspicious[i] = true;
for (int j : g[i]) {
if (!suspicious[j]) {
dfs(j);
}
}
};
dfs(k);
auto dfs2 = [&](this auto&& dfs2, int i) -> void {
vis[i] = true;
for (int j : f[i]) {
if (!vis[j]) {
suspicious[j] = false;
dfs2(j);
}
}
};
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (!suspicious[i] && !vis[i]) {
dfs2(i);
}
}
vector<int> ans;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (!suspicious[i]) {
ans.push_back(i);
}
}
return ans;
}
};func remainingMethods(n int, k int, invocations [][]int) []int {
suspicious := make([]bool, n)
vis := make([]bool, n)
f := make([][]int, n)
g := make([][]int, n)
for _, e := range invocations {
a, b := e[0], e[1]
f[a] = append(f[a], b)
f[b] = append(f[b], a)
g[a] = append(g[a], b)
}
var dfs func(int)
dfs = func(i int) {
suspicious[i] = true
for _, j := range g[i] {
if !suspicious[j] {
dfs(j)
}
}
}
dfs(k)
var dfs2 func(int)
dfs2 = func(i int) {
vis[i] = true
for _, j := range f[i] {
if !vis[j] {
suspicious[j] = false
dfs2(j)
}
}
}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
if !suspicious[i] && !vis[i] {
dfs2(i)
}
}
var ans []int
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
if !suspicious[i] {
ans = append(ans, i)
}
}
return ans
}function remainingMethods(n: number, k: number, invocations: number[][]): number[] {
const suspicious: boolean[] = Array(n).fill(false);
const vis: boolean[] = Array(n).fill(false);
const f: number[][] = Array.from({ length: n }, () => []);
const g: number[][] = Array.from({ length: n }, () => []);
for (const [a, b] of invocations) {
f[a].push(b);
f[b].push(a);
g[a].push(b);
}
const dfs = (i: number) => {
suspicious[i] = true;
for (const j of g[i]) {
if (!suspicious[j]) {
dfs(j);
}
}
};
dfs(k);
const dfs2 = (i: number) => {
vis[i] = true;
for (const j of f[i]) {
if (!vis[j]) {
suspicious[j] = false;
dfs2(j);
}
}
};
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!suspicious[i] && !vis[i]) {
dfs2(i);
}
}
return Array.from({ length: n }, (_, i) => i).filter(i => !suspicious[i]);
}