| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Hard |
1810 |
Biweekly Contest 102 Q4 |
|
There is a directed weighted graph that consists of n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1. The edges of the graph are initially represented by the given array edges where edges[i] = [fromi, toi, edgeCosti] meaning that there is an edge from fromi to toi with the cost edgeCosti.
Implement the Graph class:
Graph(int n, int[][] edges)initializes the object withnnodes and the given edges.addEdge(int[] edge)adds an edge to the list of edges whereedge = [from, to, edgeCost]. It is guaranteed that there is no edge between the two nodes before adding this one.int shortestPath(int node1, int node2)returns the minimum cost of a path fromnode1tonode2. If no path exists, return-1. The cost of a path is the sum of the costs of the edges in the path.
Example 1:
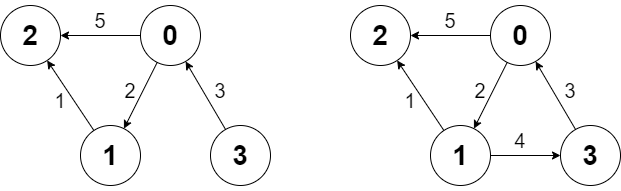
Input ["Graph", "shortestPath", "shortestPath", "addEdge", "shortestPath"] [[4, [[0, 2, 5], [0, 1, 2], [1, 2, 1], [3, 0, 3]]], [3, 2], [0, 3], [[1, 3, 4]], [0, 3]] Output [null, 6, -1, null, 6]Explanation Graph g = new Graph(4, [[0, 2, 5], [0, 1, 2], [1, 2, 1], [3, 0, 3]]); g.shortestPath(3, 2); // return 6. The shortest path from 3 to 2 in the first diagram above is 3 -> 0 -> 1 -> 2 with a total cost of 3 + 2 + 1 = 6. g.shortestPath(0, 3); // return -1. There is no path from 0 to 3. g.addEdge([1, 3, 4]); // We add an edge from node 1 to node 3, and we get the second diagram above. g.shortestPath(0, 3); // return 6. The shortest path from 0 to 3 now is 0 -> 1 -> 3 with a total cost of 2 + 4 = 6.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 1000 <= edges.length <= n * (n - 1)edges[i].length == edge.length == 30 <= fromi, toi, from, to, node1, node2 <= n - 11 <= edgeCosti, edgeCost <= 106- There are no repeated edges and no self-loops in the graph at any point.
- At most
100calls will be made foraddEdge. - At most
100calls will be made forshortestPath.
In the initialization function, we first use the adjacency matrix
In the addEdge function, we update the value of
In the shortestPath function, we use Dijsktra's algorithm to find the shortest path from node
The time complexity is shortestPath function.
class Graph:
def __init__(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]]):
self.n = n
self.g = [[inf] * n for _ in range(n)]
for f, t, c in edges:
self.g[f][t] = c
def addEdge(self, edge: List[int]) -> None:
f, t, c = edge
self.g[f][t] = c
def shortestPath(self, node1: int, node2: int) -> int:
dist = [inf] * self.n
dist[node1] = 0
vis = [False] * self.n
for _ in range(self.n):
t = -1
for j in range(self.n):
if not vis[j] and (t == -1 or dist[t] > dist[j]):
t = j
vis[t] = True
for j in range(self.n):
dist[j] = min(dist[j], dist[t] + self.g[t][j])
return -1 if dist[node2] == inf else dist[node2]
# Your Graph object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = Graph(n, edges)
# obj.addEdge(edge)
# param_2 = obj.shortestPath(node1,node2)class Graph {
private int n;
private int[][] g;
private final int inf = 1 << 29;
public Graph(int n, int[][] edges) {
this.n = n;
g = new int[n][n];
for (var f : g) {
Arrays.fill(f, inf);
}
for (int[] e : edges) {
int f = e[0], t = e[1], c = e[2];
g[f][t] = c;
}
}
public void addEdge(int[] edge) {
int f = edge[0], t = edge[1], c = edge[2];
g[f][t] = c;
}
public int shortestPath(int node1, int node2) {
int[] dist = new int[n];
boolean[] vis = new boolean[n];
Arrays.fill(dist, inf);
dist[node1] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int t = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (!vis[j] && (t == -1 || dist[t] > dist[j])) {
t = j;
}
}
vis[t] = true;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
dist[j] = Math.min(dist[j], dist[t] + g[t][j]);
}
}
return dist[node2] >= inf ? -1 : dist[node2];
}
}
/**
* Your Graph object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Graph obj = new Graph(n, edges);
* obj.addEdge(edge);
* int param_2 = obj.shortestPath(node1,node2);
*/class Graph {
public:
Graph(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
this->n = n;
g = vector<vector<int>>(n, vector<int>(n, inf));
for (auto& e : edges) {
int f = e[0], t = e[1], c = e[2];
g[f][t] = c;
}
}
void addEdge(vector<int> edge) {
int f = edge[0], t = edge[1], c = edge[2];
g[f][t] = c;
}
int shortestPath(int node1, int node2) {
vector<bool> vis(n);
vector<int> dist(n, inf);
dist[node1] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int t = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (!vis[j] && (t == -1 || dist[t] > dist[j])) {
t = j;
}
}
vis[t] = true;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
dist[j] = min(dist[j], dist[t] + g[t][j]);
}
}
return dist[node2] >= inf ? -1 : dist[node2];
}
private:
vector<vector<int>> g;
int n;
const int inf = 1 << 29;
};
/**
* Your Graph object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Graph* obj = new Graph(n, edges);
* obj->addEdge(edge);
* int param_2 = obj->shortestPath(node1,node2);
*/const inf = 1 << 29
type Graph struct {
g [][]int
}
func Constructor(n int, edges [][]int) Graph {
g := make([][]int, n)
for i := range g {
g[i] = make([]int, n)
for j := range g[i] {
g[i][j] = inf
}
}
for _, e := range edges {
f, t, c := e[0], e[1], e[2]
g[f][t] = c
}
return Graph{g}
}
func (this *Graph) AddEdge(edge []int) {
f, t, c := edge[0], edge[1], edge[2]
this.g[f][t] = c
}
func (this *Graph) ShortestPath(node1 int, node2 int) int {
n := len(this.g)
dist := make([]int, n)
for i := range dist {
dist[i] = inf
}
vis := make([]bool, n)
dist[node1] = 0
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
t := -1
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if !vis[j] && (t == -1 || dist[t] > dist[j]) {
t = j
}
}
vis[t] = true
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
dist[j] = min(dist[j], dist[t]+this.g[t][j])
}
}
if dist[node2] >= inf {
return -1
}
return dist[node2]
}
/**
* Your Graph object will be instantiated and called as such:
* obj := Constructor(n, edges);
* obj.AddEdge(edge);
* param_2 := obj.ShortestPath(node1,node2);
*/class Graph {
private g: number[][] = [];
private inf: number = 1 << 29;
constructor(n: number, edges: number[][]) {
this.g = Array.from({ length: n }, () => Array(n).fill(this.inf));
for (const [f, t, c] of edges) {
this.g[f][t] = c;
}
}
addEdge(edge: number[]): void {
const [f, t, c] = edge;
this.g[f][t] = c;
}
shortestPath(node1: number, node2: number): number {
const n = this.g.length;
const dist: number[] = new Array(n).fill(this.inf);
dist[node1] = 0;
const vis: boolean[] = new Array(n).fill(false);
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
let t = -1;
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (!vis[j] && (t === -1 || dist[j] < dist[t])) {
t = j;
}
}
vis[t] = true;
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
dist[j] = Math.min(dist[j], dist[t] + this.g[t][j]);
}
}
return dist[node2] >= this.inf ? -1 : dist[node2];
}
}
/**
* Your Graph object will be instantiated and called as such:
* var obj = new Graph(n, edges)
* obj.addEdge(edge)
* var param_2 = obj.shortestPath(node1,node2)
*/public class Graph {
private int n;
private int[,] g;
private readonly int inf = 1 << 29;
public Graph(int n, int[][] edges) {
this.n = n;
g = new int[n, n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
g[i, j] = inf;
}
}
foreach (var e in edges) {
int f = e[0], t = e[1], c = e[2];
g[f, t] = c;
}
}
public void AddEdge(int[] edge) {
int f = edge[0], t = edge[1], c = edge[2];
g[f, t] = c;
}
public int ShortestPath(int node1, int node2) {
int[] dist = new int[n];
bool[] vis = new bool[n];
Array.Fill(dist, inf);
dist[node1] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int t = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (!vis[j] && (t == -1 || dist[t] > dist[j])) {
t = j;
}
}
vis[t] = true;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
dist[j] = Math.Min(dist[j], dist[t] + g[t, j]);
}
}
return dist[node2] >= inf ? -1 : dist[node2];
}
}
/**
* Your Graph object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Graph obj = new Graph(n, edges);
* obj.AddEdge(edge);
* int param_2 = obj.ShortestPath(node1,node2);
*/