| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
1421 |
Weekly Contest 300 Q2 |
|
You are given two integers m and n, which represent the dimensions of a matrix.
You are also given the head of a linked list of integers.
Generate an m x n matrix that contains the integers in the linked list presented in spiral order (clockwise), starting from the top-left of the matrix. If there are remaining empty spaces, fill them with -1.
Return the generated matrix.
Example 1:
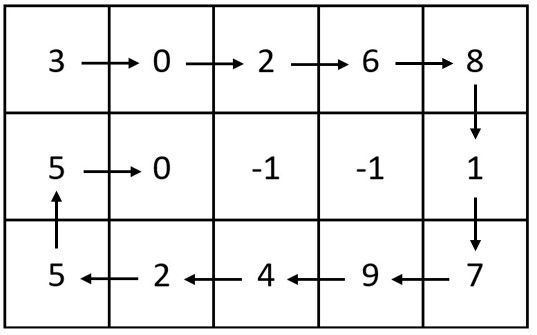
Input: m = 3, n = 5, head = [3,0,2,6,8,1,7,9,4,2,5,5,0] Output: [[3,0,2,6,8],[5,0,-1,-1,1],[5,2,4,9,7]] Explanation: The diagram above shows how the values are printed in the matrix. Note that the remaining spaces in the matrix are filled with -1.
Example 2:
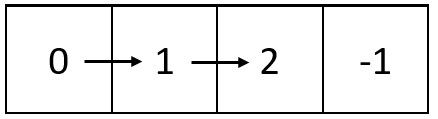
Input: m = 1, n = 4, head = [0,1,2] Output: [[0,1,2,-1]] Explanation: The diagram above shows how the values are printed from left to right in the matrix. The last space in the matrix is set to -1.
Constraints:
1 <= m, n <= 1051 <= m * n <= 105- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[1, m * n]. 0 <= Node.val <= 1000
We define a two-dimensional array
Then we start traversing the linked list. Each time we traverse a node, we fill the current node's value into
Otherwise, we need to find the position of the next element. We can calculate the next position
After traversing the linked list, we get a spiral matrix and return it.
The time complexity is
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def spiralMatrix(self, m: int, n: int, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> List[List[int]]:
ans = [[-1] * n for _ in range(m)]
i = j = k = 0
dirs = (0, 1, 0, -1, 0)
while 1:
ans[i][j] = head.val
head = head.next
if head is None:
break
while 1:
x, y = i + dirs[k], j + dirs[k + 1]
if 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n and ans[x][y] == -1:
i, j = x, y
break
k = (k + 1) % 4
return ans/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int[][] spiralMatrix(int m, int n, ListNode head) {
int[][] ans = new int[m][n];
for (var row : ans) {
Arrays.fill(row, -1);
}
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
final int[] dirs = {0, 1, 0, -1, 0};
while (true) {
ans[i][j] = head.val;
head = head.next;
if (head == null) {
break;
}
while (true) {
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && ans[x][y] == -1) {
i = x;
j = y;
break;
}
k = (k + 1) % 4;
}
}
return ans;
}
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> spiralMatrix(int m, int n, ListNode* head) {
vector<vector<int>> ans(m, vector<int>(n, -1));
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
const int dirs[5] = {0, 1, 0, -1, 0};
while (1) {
ans[i][j] = head->val;
head = head->next;
if (!head) {
break;
}
while (1) {
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && ans[x][y] == -1) {
i = x;
j = y;
break;
}
k = (k + 1) % 4;
}
}
return ans;
}
};/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func spiralMatrix(m int, n int, head *ListNode) [][]int {
ans := make([][]int, m)
for i := range ans {
ans[i] = make([]int, n)
for j := range ans[i] {
ans[i][j] = -1
}
}
i, j, k := 0, 0, 0
dirs := [5]int{0, 1, 0, -1, 0}
for {
ans[i][j] = head.Val
if head = head.Next; head == nil {
break
}
for {
x, y := i+dirs[k], j+dirs[k+1]
if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && ans[x][y] == -1 {
i, j = x, y
break
}
k = (k + 1) % 4
}
}
return ans
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* val: number
* next: ListNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
* }
*/
function spiralMatrix(m: number, n: number, head: ListNode | null): number[][] {
const ans: number[][] = Array.from({ length: m }, () => Array(n).fill(-1));
const dirs: number[] = [0, 1, 0, -1, 0];
let [i, j, k] = [0, 0, 0];
while (1) {
ans[i][j] = head.val;
head = head.next;
if (!head) {
break;
}
while (1) {
const [x, y] = [i + dirs[k], j + dirs[k + 1]];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && ans[x][y] === -1) {
i = x;
j = y;
break;
}
k = (k + 1) % 4;
}
}
return ans;
}