| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
1868 |
Weekly Contest 285 Q3 |
|
Alice and Bob are opponents in an archery competition. The competition has set the following rules:
- Alice first shoots
numArrowsarrows and then Bob shootsnumArrowsarrows. - The points are then calculated as follows:
- The target has integer scoring sections ranging from
0to11inclusive. - For each section of the target with score
k(in between0to11), say Alice and Bob have shotakandbkarrows on that section respectively. Ifak >= bk, then Alice takeskpoints. Ifak < bk, then Bob takeskpoints. - However, if
ak == bk == 0, then nobody takeskpoints.
- The target has integer scoring sections ranging from
-
For example, if Alice and Bob both shot
2arrows on the section with score11, then Alice takes11points. On the other hand, if Alice shot0arrows on the section with score11and Bob shot2arrows on that same section, then Bob takes11points.
You are given the integer numArrows and an integer array aliceArrows of size 12, which represents the number of arrows Alice shot on each scoring section from 0 to 11. Now, Bob wants to maximize the total number of points he can obtain.
Return the array bobArrows which represents the number of arrows Bob shot on each scoring section from 0 to 11. The sum of the values in bobArrows should equal numArrows.
If there are multiple ways for Bob to earn the maximum total points, return any one of them.
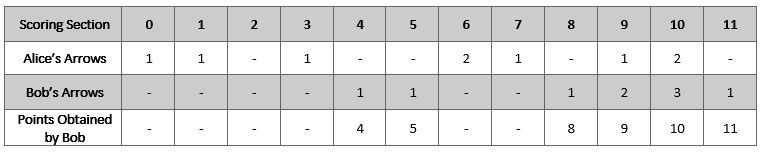
Example 1:
Input: numArrows = 9, aliceArrows = [1,1,0,1,0,0,2,1,0,1,2,0] Output: [0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,2,3,1] Explanation: The table above shows how the competition is scored. Bob earns a total point of 4 + 5 + 8 + 9 + 10 + 11 = 47. It can be shown that Bob cannot obtain a score higher than 47 points.
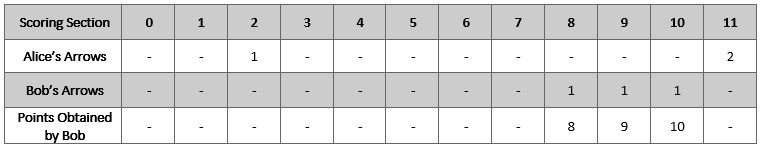
Example 2:
Input: numArrows = 3, aliceArrows = [0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,2] Output: [0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0] Explanation: The table above shows how the competition is scored. Bob earns a total point of 8 + 9 + 10 = 27. It can be shown that Bob cannot obtain a score higher than 27 points.
Constraints:
1 <= numArrows <= 105aliceArrows.length == bobArrows.length == 120 <= aliceArrows[i], bobArrows[i] <= numArrowssum(aliceArrows[i]) == numArrows
class Solution:
def maximumBobPoints(self, numArrows: int, aliceArrows: List[int]) -> List[int]:
n = len(aliceArrows)
state = 0
mx = -1
for mask in range(1 << n):
cnt = points = 0
for i, alice in enumerate(aliceArrows):
if (mask >> i) & 1:
cnt += alice + 1
points += i
if cnt <= numArrows and mx < points:
state = mask
mx = points
ans = [0] * n
for i, alice in enumerate(aliceArrows):
if (state >> i) & 1:
ans[i] = alice + 1
numArrows -= ans[i]
ans[0] = numArrows
return ansclass Solution {
public int[] maximumBobPoints(int numArrows, int[] aliceArrows) {
int n = aliceArrows.length;
int mx = -1;
int state = 0;
for (int mask = 1; mask < 1 << n; ++mask) {
int cnt = 0, points = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (((mask >> i) & 1) == 1) {
cnt += aliceArrows[i] + 1;
points += i;
}
}
if (cnt <= numArrows && mx < points) {
state = mask;
mx = points;
}
}
int[] ans = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (((state >> i) & 1) == 1) {
ans[i] = aliceArrows[i] + 1;
numArrows -= ans[i];
}
}
ans[0] += numArrows;
return ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<int> maximumBobPoints(int numArrows, vector<int>& aliceArrows) {
int n = aliceArrows.size();
int state = 0, mx = -1;
for (int mask = 1; mask < 1 << n; ++mask) {
int cnt = 0, points = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if ((mask >> i) & 1) {
cnt += aliceArrows[i] + 1;
points += i;
}
}
if (cnt <= numArrows && mx < points) {
state = mask;
mx = points;
}
}
vector<int> ans(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if ((state >> i) & 1) {
ans[i] = aliceArrows[i] + 1;
numArrows -= ans[i];
}
}
ans[0] += numArrows;
return ans;
}
};func maximumBobPoints(numArrows int, aliceArrows []int) []int {
n := len(aliceArrows)
state, mx := 0, -1
for mask := 1; mask < 1<<n; mask++ {
cnt, points := 0, 0
for i, alice := range aliceArrows {
if (mask>>i)&1 == 1 {
cnt += alice + 1
points += i
}
}
if cnt <= numArrows && mx < points {
state = mask
mx = points
}
}
ans := make([]int, n)
for i, alice := range aliceArrows {
if (state>>i)&1 == 1 {
ans[i] = alice + 1
numArrows -= ans[i]
}
}
ans[0] += numArrows
return ans
}function maximumBobPoints(numArrows: number, aliceArrows: number[]): number[] {
const dfs = (arr: number[], i: number, c: number): number[] => {
if (i < 0 || c === 0) {
arr[0] += c;
return arr;
}
const a1 = dfs([...arr], i - 1, c);
if (c > aliceArrows[i]) {
arr[i] = aliceArrows[i] + 1;
const a2 = dfs(arr, i - 1, c - aliceArrows[i] - 1);
if (
a2.reduce((p, v, i) => p + (v > 0 ? i : 0), 0) >=
a1.reduce((p, v, i) => p + (v > 0 ? i : 0), 0)
) {
return a2;
}
}
return a1;
};
return dfs(new Array(12).fill(0), 11, numArrows);
}impl Solution {
fn dfs(alice_arrows: &Vec<i32>, mut res: Vec<i32>, count: i32, i: usize) -> Vec<i32> {
if i == 0 || count == 0 {
res[0] += count;
return res;
}
let r1 = Self::dfs(alice_arrows, res.clone(), count, i - 1);
if count > alice_arrows[i] {
res[i] = alice_arrows[i] + 1;
let r2 = Self::dfs(alice_arrows, res, count - alice_arrows[i] - 1, i - 1);
if r2
.iter()
.enumerate()
.map(|(i, v)| if v > &0 { i } else { 0 })
.sum::<usize>()
> r1.iter()
.enumerate()
.map(|(i, v)| if v > &0 { i } else { 0 })
.sum::<usize>()
{
return r2;
}
}
r1
}
pub fn maximum_bob_points(num_arrows: i32, alice_arrows: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<i32> {
Self::dfs(&alice_arrows, vec![0; 12], num_arrows, 11)
}
}