| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Hard |
2123 |
Weekly Contest 254 Q4 |
|
There is a 1-based binary matrix where 0 represents land and 1 represents water. You are given integers row and col representing the number of rows and columns in the matrix, respectively.
Initially on day 0, the entire matrix is land. However, each day a new cell becomes flooded with water. You are given a 1-based 2D array cells, where cells[i] = [ri, ci] represents that on the ith day, the cell on the rith row and cith column (1-based coordinates) will be covered with water (i.e., changed to 1).
You want to find the last day that it is possible to walk from the top to the bottom by only walking on land cells. You can start from any cell in the top row and end at any cell in the bottom row. You can only travel in the four cardinal directions (left, right, up, and down).
Return the last day where it is possible to walk from the top to the bottom by only walking on land cells.
Example 1:
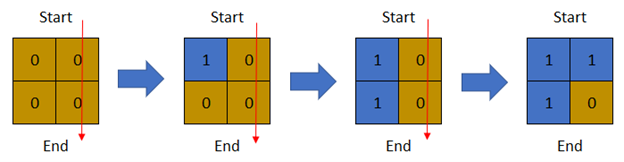
Input: row = 2, col = 2, cells = [[1,1],[2,1],[1,2],[2,2]] Output: 2 Explanation: The above image depicts how the matrix changes each day starting from day 0. The last day where it is possible to cross from top to bottom is on day 2.
Example 2:
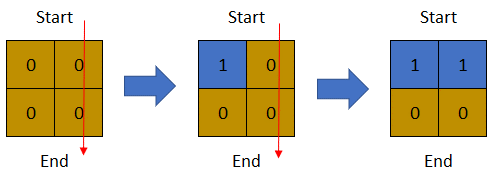
Input: row = 2, col = 2, cells = [[1,1],[1,2],[2,1],[2,2]] Output: 1 Explanation: The above image depicts how the matrix changes each day starting from day 0. The last day where it is possible to cross from top to bottom is on day 1.
Example 3:
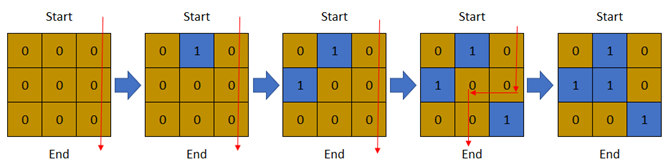
Input: row = 3, col = 3, cells = [[1,2],[2,1],[3,3],[2,2],[1,1],[1,3],[2,3],[3,2],[3,1]] Output: 3 Explanation: The above image depicts how the matrix changes each day starting from day 0. The last day where it is possible to cross from top to bottom is on day 3.
Constraints:
2 <= row, col <= 2 * 1044 <= row * col <= 2 * 104cells.length == row * col1 <= ri <= row1 <= ci <= col- All the values of
cellsare unique.
We note that if we can walk from the top row to the bottom row on day
We define the left boundary of the binary search as
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def latestDayToCross(self, row: int, col: int, cells: List[List[int]]) -> int:
def check(k: int) -> bool:
g = [[0] * col for _ in range(row)]
for i, j in cells[:k]:
g[i - 1][j - 1] = 1
q = [(0, j) for j in range(col) if g[0][j] == 0]
for x, y in q:
if x == row - 1:
return True
for a, b in pairwise(dirs):
nx, ny = x + a, y + b
if 0 <= nx < row and 0 <= ny < col and g[nx][ny] == 0:
q.append((nx, ny))
g[nx][ny] = 1
return False
n = row * col
l, r = 1, n
dirs = (-1, 0, 1, 0, -1)
while l < r:
mid = (l + r + 1) >> 1
if check(mid):
l = mid
else:
r = mid - 1
return lclass Solution {
private int[][] cells;
private int m;
private int n;
public int latestDayToCross(int row, int col, int[][] cells) {
int l = 1, r = cells.length;
this.cells = cells;
this.m = row;
this.n = col;
while (l < r) {
int mid = (l + r + 1) >> 1;
if (check(mid)) {
l = mid;
} else {
r = mid - 1;
}
}
return l;
}
private boolean check(int k) {
int[][] g = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
g[cells[i][0] - 1][cells[i][1] - 1] = 1;
}
final int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
Deque<int[]> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (g[0][j] == 0) {
q.offer(new int[] {0, j});
g[0][j] = 1;
}
}
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] p = q.poll();
int x = p[0], y = p[1];
if (x == m - 1) {
return true;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = x + dirs[i], ny = y + dirs[i + 1];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n && g[nx][ny] == 0) {
q.offer(new int[] {nx, ny});
g[nx][ny] = 1;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int latestDayToCross(int row, int col, vector<vector<int>>& cells) {
int l = 1, r = cells.size();
int g[row][col];
int dirs[5] = {0, 1, 0, -1, 0};
auto check = [&](int k) -> bool {
memset(g, 0, sizeof(g));
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {
g[cells[i][0] - 1][cells[i][1] - 1] = 1;
}
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
for (int j = 0; j < col; ++j) {
if (g[0][j] == 0) {
q.emplace(0, j);
g[0][j] = 1;
}
}
while (!q.empty()) {
auto [x, y] = q.front();
q.pop();
if (x == row - 1) {
return true;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
int nx = x + dirs[i];
int ny = y + dirs[i + 1];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < row && ny >= 0 && ny < col && g[nx][ny] == 0) {
q.emplace(nx, ny);
g[nx][ny] = 1;
}
}
}
return false;
};
while (l < r) {
int mid = (l + r + 1) >> 1;
if (check(mid)) {
l = mid;
} else {
r = mid - 1;
}
}
return l;
}
};func latestDayToCross(row int, col int, cells [][]int) int {
l, r := 1, len(cells)
dirs := [5]int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}
check := func(k int) bool {
g := make([][]int, row)
for i := range g {
g[i] = make([]int, col)
}
for i := 0; i < k; i++ {
g[cells[i][0]-1][cells[i][1]-1] = 1
}
q := [][2]int{}
for j := 0; j < col; j++ {
if g[0][j] == 0 {
g[0][j] = 1
q = append(q, [2]int{0, j})
}
}
for len(q) > 0 {
x, y := q[0][0], q[0][1]
q = q[1:]
if x == row-1 {
return true
}
for i := 0; i < 4; i++ {
nx, ny := x+dirs[i], y+dirs[i+1]
if nx >= 0 && nx < row && ny >= 0 && ny < col && g[nx][ny] == 0 {
g[nx][ny] = 1
q = append(q, [2]int{nx, ny})
}
}
}
return false
}
for l < r {
mid := (l + r + 1) >> 1
if check(mid) {
l = mid
} else {
r = mid - 1
}
}
return l
}function latestDayToCross(row: number, col: number, cells: number[][]): number {
let [l, r] = [1, cells.length];
const check = (k: number): boolean => {
const g: number[][] = Array.from({ length: row }, () => Array(col).fill(0));
for (let i = 0; i < k; ++i) {
const [x, y] = cells[i];
g[x - 1][y - 1] = 1;
}
const q: number[][] = [];
for (let j = 0; j < col; ++j) {
if (g[0][j] === 0) {
q.push([0, j]);
g[0][j] = 1;
}
}
const dirs: number[] = [-1, 0, 1, 0, -1];
for (const [x, y] of q) {
if (x === row - 1) {
return true;
}
for (let i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
const nx = x + dirs[i];
const ny = y + dirs[i + 1];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < row && ny >= 0 && ny < col && g[nx][ny] === 0) {
q.push([nx, ny]);
g[nx][ny] = 1;
}
}
}
return false;
};
while (l < r) {
const mid = (l + r + 1) >> 1;
if (check(mid)) {
l = mid;
} else {
r = mid - 1;
}
}
return l;
}We can first initialize all land cells as
The time complexity is
class UnionFind:
def __init__(self, n):
self.p = list(range(n))
self.size = [1] * n
def find(self, x):
if self.p[x] != x:
self.p[x] = self.find(self.p[x])
return self.p[x]
def union(self, a, b):
pa, pb = self.find(a), self.find(b)
if pa == pb:
return False
if self.size[pa] > self.size[pb]:
self.p[pb] = pa
self.size[pa] += self.size[pb]
else:
self.p[pa] = pb
self.size[pb] += self.size[pa]
return True
class Solution:
def latestDayToCross(self, row: int, col: int, cells: List[List[int]]) -> int:
mn = len(cells)
uf = UnionFind(mn + 2)
s, t = mn, mn + 1
dirs = (-1, 0, 1, 0, -1)
g = [[1] * col for _ in range(row)]
for i in range(mn - 1, -1, -1):
x, y = cells[i][0] - 1, cells[i][1] - 1
g[x][y] = 0
for a, b in pairwise(dirs):
nx, ny = x + a, y + b
if 0 <= nx < row and 0 <= ny < col and g[nx][ny] == 0:
uf.union(x * col + y, nx * col + ny)
if x == 0:
uf.union(y, s)
if x == row - 1:
uf.union(x * col + y, t)
if uf.find(s) == uf.find(t):
return iclass UnionFind {
private final int[] p;
private final int[] size;
public UnionFind(int n) {
p = new int[n];
size = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
p[i] = i;
size[i] = 1;
}
}
public int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
}
public boolean union(int a, int b) {
int pa = find(a), pb = find(b);
if (pa == pb) {
return false;
}
if (size[pa] > size[pb]) {
p[pb] = pa;
size[pa] += size[pb];
} else {
p[pa] = pb;
size[pb] += size[pa];
}
return true;
}
}
class Solution {
public int latestDayToCross(int row, int col, int[][] cells) {
int mn = cells.length;
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(mn + 2);
int s = mn, t = mn + 1;
int[][] g = new int[row][col];
for (var e : g) {
Arrays.fill(e, 1);
}
final int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
for (int i = mn - 1;; --i) {
int x = cells[i][0] - 1, y = cells[i][1] - 1;
g[x][y] = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
int nx = x + dirs[j], ny = y + dirs[j + 1];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < row && ny >= 0 && ny < col && g[nx][ny] == 0) {
uf.union(x * col + y, nx * col + ny);
}
}
if (x == 0) {
uf.union(s, x * col + y);
}
if (x == row - 1) {
uf.union(t, x * col + y);
}
if (uf.find(s) == uf.find(t)) {
return i;
}
}
}
}class UnionFind {
public:
UnionFind(int n) {
p = vector<int>(n);
size = vector<int>(n, 1);
iota(p.begin(), p.end(), 0);
}
bool unite(int a, int b) {
int pa = find(a), pb = find(b);
if (pa == pb) {
return false;
}
if (size[pa] > size[pb]) {
p[pb] = pa;
size[pa] += size[pb];
} else {
p[pa] = pb;
size[pb] += size[pa];
}
return true;
}
int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
}
private:
vector<int> p, size;
};
class Solution {
public:
int latestDayToCross(int row, int col, vector<vector<int>>& cells) {
int mn = cells.size();
UnionFind uf(mn + 2);
int s = mn, t = mn + 1;
vector<vector<int>> g(row, vector<int>(col, 1));
const int dirs[5] = {0, 1, 0, -1, 0};
for (int i = mn - 1;; --i) {
int x = cells[i][0] - 1, y = cells[i][1] - 1;
g[x][y] = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
int nx = x + dirs[j], ny = y + dirs[j + 1];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < row && ny >= 0 && ny < col && g[nx][ny] == 0) {
uf.unite(x * col + y, nx * col + ny);
}
}
if (x == 0) {
uf.unite(s, x * col + y);
}
if (x == row - 1) {
uf.unite(t, x * col + y);
}
if (uf.find(s) == uf.find(t)) {
return i;
}
}
}
};type unionFind struct {
p, size []int
}
func newUnionFind(n int) *unionFind {
p := make([]int, n)
size := make([]int, n)
for i := range p {
p[i] = i
size[i] = 1
}
return &unionFind{p, size}
}
func (uf *unionFind) find(x int) int {
if uf.p[x] != x {
uf.p[x] = uf.find(uf.p[x])
}
return uf.p[x]
}
func (uf *unionFind) union(a, b int) bool {
pa, pb := uf.find(a), uf.find(b)
if pa == pb {
return false
}
if uf.size[pa] > uf.size[pb] {
uf.p[pb] = pa
uf.size[pa] += uf.size[pb]
} else {
uf.p[pa] = pb
uf.size[pb] += uf.size[pa]
}
return true
}
func latestDayToCross(row int, col int, cells [][]int) int {
mn := len(cells)
uf := newUnionFind(mn + 2)
s, t := mn, mn+1
g := make([][]int, row)
for i := range g {
g[i] = make([]int, col)
for j := range g[i] {
g[i][j] = 1
}
}
dirs := [5]int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}
for i := mn - 1; ; i-- {
x, y := cells[i][0]-1, cells[i][1]-1
g[x][y] = 0
for j := 0; j < 4; j++ {
nx, ny := x+dirs[j], y+dirs[j+1]
if nx >= 0 && nx < row && ny >= 0 && ny < col && g[nx][ny] == 0 {
uf.union(x*col+y, nx*col+ny)
}
}
if x == 0 {
uf.union(s, x*col+y)
}
if x == row-1 {
uf.union(t, x*col+y)
}
if uf.find(s) == uf.find(t) {
return i
}
}
}class UnionFind {
p: number[];
size: number[];
constructor(n: number) {
this.p = Array(n)
.fill(0)
.map((_, i) => i);
this.size = Array(n).fill(1);
}
find(x: number): number {
if (this.p[x] !== x) {
this.p[x] = this.find(this.p[x]);
}
return this.p[x];
}
union(a: number, b: number): boolean {
const [pa, pb] = [this.find(a), this.find(b)];
if (pa === pb) {
return false;
}
if (this.size[pa] > this.size[pb]) {
this.p[pb] = pa;
this.size[pa] += this.size[pb];
} else {
this.p[pa] = pb;
this.size[pb] += this.size[pa];
}
return true;
}
}
function latestDayToCross(row: number, col: number, cells: number[][]): number {
const mn = cells.length;
const uf = new UnionFind(row * col + 2);
const [s, t] = [mn, mn + 1];
const g: number[][] = Array.from({ length: row }, () => Array(col).fill(1));
const dirs: number[] = [-1, 0, 1, 0, -1];
for (let i = mn - 1; ; --i) {
const [x, y] = [cells[i][0] - 1, cells[i][1] - 1];
g[x][y] = 0;
for (let j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
const [nx, ny] = [x + dirs[j], y + dirs[j + 1]];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < row && ny >= 0 && ny < col && g[nx][ny] === 0) {
uf.union(x * col + y, nx * col + ny);
}
}
if (x === 0) {
uf.union(s, y);
}
if (x === row - 1) {
uf.union(t, x * col + y);
}
if (uf.find(s) === uf.find(t)) {
return i;
}
}
}