| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Easy |
1286 |
Weekly Contest 232 Q2 |
|
There is an undirected star graph consisting of n nodes labeled from 1 to n. A star graph is a graph where there is one center node and exactly n - 1 edges that connect the center node with every other node.
You are given a 2D integer array edges where each edges[i] = [ui, vi] indicates that there is an edge between the nodes ui and vi. Return the center of the given star graph.
Example 1:
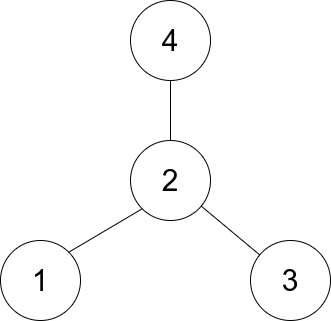
Input: edges = [[1,2],[2,3],[4,2]] Output: 2 Explanation: As shown in the figure above, node 2 is connected to every other node, so 2 is the center.
Example 2:
Input: edges = [[1,2],[5,1],[1,3],[1,4]] Output: 1
Constraints:
3 <= n <= 105edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 21 <= ui, vi <= nui != vi- The given
edgesrepresent a valid star graph.
The characteristic of the center point is that it is connected to all other points. Therefore, as long as we compare the points of the first two edges, if there are the same points, then this point is the center point.
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def findCenter(self, edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:
return edges[0][0] if edges[0][0] in edges[1] else edges[0][1]class Solution {
public int findCenter(int[][] edges) {
int a = edges[0][0], b = edges[0][1];
int c = edges[1][0], d = edges[1][1];
return a == c || a == d ? a : b;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int findCenter(vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
int a = edges[0][0], b = edges[0][1];
int c = edges[1][0], d = edges[1][1];
return a == c || a == d ? a : b;
}
};func findCenter(edges [][]int) int {
a, b := edges[0][0], edges[0][1]
c, d := edges[1][0], edges[1][1]
if a == c || a == d {
return a
}
return b
}function findCenter(edges: number[][]): number {
for (let num of edges[0]) {
if (edges[1].includes(num)) {
return num;
}
}
}impl Solution {
pub fn find_center(edges: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
if edges[0][0] == edges[1][0] || edges[0][0] == edges[1][1] {
return edges[0][0];
}
edges[0][1]
}
}/**
* @param {number[][]} edges
* @return {number}
*/
var findCenter = function (edges) {
const [a, b] = edges[0];
const [c, d] = edges[1];
return a == c || a == d ? a : b;
};