| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
1548 |
Biweekly Contest 18 Q3 |
|
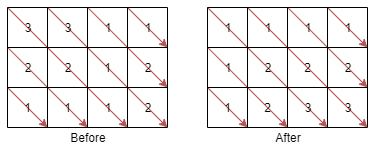
A matrix diagonal is a diagonal line of cells starting from some cell in either the topmost row or leftmost column and going in the bottom-right direction until reaching the matrix's end. For example, the matrix diagonal starting from mat[2][0], where mat is a 6 x 3 matrix, includes cells mat[2][0], mat[3][1], and mat[4][2].
Given an m x n matrix mat of integers, sort each matrix diagonal in ascending order and return the resulting matrix.
Example 1:
Input: mat = [[3,3,1,1],[2,2,1,2],[1,1,1,2]] Output: [[1,1,1,1],[1,2,2,2],[1,2,3,3]]
Example 2:
Input: mat = [[11,25,66,1,69,7],[23,55,17,45,15,52],[75,31,36,44,58,8],[22,27,33,25,68,4],[84,28,14,11,5,50]] Output: [[5,17,4,1,52,7],[11,11,25,45,8,69],[14,23,25,44,58,15],[22,27,31,36,50,66],[84,28,75,33,55,68]]
Constraints:
m == mat.lengthn == mat[i].length1 <= m, n <= 1001 <= mat[i][j] <= 100
We can treat each diagonal of the matrix as an array, sort these arrays, and then fill the sorted elements back into the original matrix.
Specifically, we denote the number of rows in the matrix as
Finally, we fill the sorted elements of each diagonal back into the original matrix.
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def diagonalSort(self, mat: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
m, n = len(mat), len(mat[0])
g = [[] for _ in range(m + n)]
for i, row in enumerate(mat):
for j, x in enumerate(row):
g[m - i + j].append(x)
for e in g:
e.sort(reverse=True)
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
mat[i][j] = g[m - i + j].pop()
return matclass Solution {
public int[][] diagonalSort(int[][] mat) {
int m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length;
List<Integer>[] g = new List[m + n];
Arrays.setAll(g, k -> new ArrayList<>());
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
g[m - i + j].add(mat[i][j]);
}
}
for (var e : g) {
Collections.sort(e, (a, b) -> b - a);
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
mat[i][j] = g[m - i + j].removeLast();
}
}
return mat;
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> diagonalSort(vector<vector<int>>& mat) {
int m = mat.size(), n = mat[0].size();
vector<int> g[m + n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
g[m - i + j].push_back(mat[i][j]);
}
}
for (auto& e : g) {
sort(e.rbegin(), e.rend());
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
mat[i][j] = g[m - i + j].back();
g[m - i + j].pop_back();
}
}
return mat;
}
};func diagonalSort(mat [][]int) [][]int {
m, n := len(mat), len(mat[0])
g := make([][]int, m+n)
for i, row := range mat {
for j, x := range row {
g[m-i+j] = append(g[m-i+j], x)
}
}
for _, e := range g {
sort.Sort(sort.Reverse(sort.IntSlice(e)))
}
for i, row := range mat {
for j := range row {
k := len(g[m-i+j])
mat[i][j] = g[m-i+j][k-1]
g[m-i+j] = g[m-i+j][:k-1]
}
}
return mat
}function diagonalSort(mat: number[][]): number[][] {
const [m, n] = [mat.length, mat[0].length];
const g: number[][] = Array.from({ length: m + n }, () => []);
for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
g[m - i + j].push(mat[i][j]);
}
}
for (const e of g) {
e.sort((a, b) => b - a);
}
for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
mat[i][j] = g[m - i + j].pop()!;
}
}
return mat;
}impl Solution {
pub fn diagonal_sort(mut mat: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
let m = mat.len();
let n = mat[0].len();
let mut g: Vec<Vec<i32>> = vec![vec![]; m + n];
for i in 0..m {
for j in 0..n {
g[m - i + j].push(mat[i][j]);
}
}
for e in &mut g {
e.sort_by(|a, b| b.cmp(a));
}
for i in 0..m {
for j in 0..n {
mat[i][j] = g[m - i + j].pop().unwrap();
}
}
mat
}
}public class Solution {
public int[][] DiagonalSort(int[][] mat) {
int m = mat.Length;
int n = mat[0].Length;
List<List<int>> g = new List<List<int>>();
for (int i = 0; i < m + n; i++) {
g.Add(new List<int>());
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
g[m - i + j].Add(mat[i][j]);
}
}
foreach (var e in g) {
e.Sort((a, b) => b.CompareTo(a));
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
int val = g[m - i + j][g[m - i + j].Count - 1];
g[m - i + j].RemoveAt(g[m - i + j].Count - 1);
mat[i][j] = val;
}
}
return mat;
}
}