| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
中等 |
1652 |
第 170 场周赛 Q3 |
|
有 n 个人,每个人都有一个 0 到 n-1 的唯一 id 。
给你数组 watchedVideos 和 friends ,其中 watchedVideos[i] 和 friends[i] 分别表示 id = i 的人观看过的视频列表和他的好友列表。
Level 1 的视频包含所有你好友观看过的视频,level 2 的视频包含所有你好友的好友观看过的视频,以此类推。一般的,Level 为 k 的视频包含所有从你出发,最短距离为 k 的好友观看过的视频。
给定你的 id 和一个 level 值,请你找出所有指定 level 的视频,并将它们按观看频率升序返回。如果有频率相同的视频,请将它们按字母顺序从小到大排列。
示例 1:
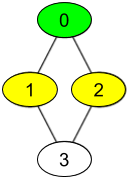
输入:watchedVideos = [["A","B"],["C"],["B","C"],["D"]], friends = [[1,2],[0,3],[0,3],[1,2]], id = 0, level = 1 输出:["B","C"] 解释: 你的 id 为 0(绿色),你的朋友包括(黄色): id 为 1 -> watchedVideos = ["C"] id 为 2 -> watchedVideos = ["B","C"] 你朋友观看过视频的频率为: B -> 1 C -> 2
示例 2:
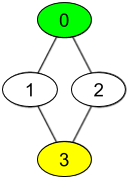
输入:watchedVideos = [["A","B"],["C"],["B","C"],["D"]], friends = [[1,2],[0,3],[0,3],[1,2]], id = 0, level = 2 输出:["D"] 解释: 你的 id 为 0(绿色),你朋友的朋友只有一个人,他的 id 为 3(黄色)。
提示:
n == watchedVideos.length == friends.length2 <= n <= 1001 <= watchedVideos[i].length <= 1001 <= watchedVideos[i][j].length <= 80 <= friends[i].length < n0 <= friends[i][j] < n0 <= id < n1 <= level < n- 如果
friends[i]包含j,那么friends[j]包含i
我们可以使用广度优先搜索的方法,从
具体地,我们可以使用一个队列
然后,我们使用一个哈希表
时间复杂度
class Solution:
def watchedVideosByFriends(
self,
watchedVideos: List[List[str]],
friends: List[List[int]],
id: int,
level: int,
) -> List[str]:
q = deque([id])
vis = {id}
for _ in range(level):
for _ in range(len(q)):
i = q.popleft()
for j in friends[i]:
if j not in vis:
vis.add(j)
q.append(j)
cnt = Counter()
for i in q:
for v in watchedVideos[i]:
cnt[v] += 1
return sorted(cnt.keys(), key=lambda k: (cnt[k], k))class Solution {
public List<String> watchedVideosByFriends(
List<List<String>> watchedVideos, int[][] friends, int id, int level) {
Deque<Integer> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
q.offer(id);
int n = friends.length;
boolean[] vis = new boolean[n];
vis[id] = true;
while (level-- > 0) {
for (int k = q.size(); k > 0; --k) {
int i = q.poll();
for (int j : friends[i]) {
if (!vis[j]) {
vis[j] = true;
q.offer(j);
}
}
}
}
Map<String, Integer> cnt = new HashMap<>();
for (int i : q) {
for (var v : watchedVideos.get(i)) {
cnt.merge(v, 1, Integer::sum);
}
}
List<String> ans = new ArrayList<>(cnt.keySet());
ans.sort((a, b) -> {
int x = cnt.get(a), y = cnt.get(b);
return x == y ? a.compareTo(b) : Integer.compare(x, y);
});
return ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<string> watchedVideosByFriends(vector<vector<string>>& watchedVideos, vector<vector<int>>& friends, int id, int level) {
queue<int> q{{id}};
int n = friends.size();
vector<bool> vis(n);
vis[id] = true;
while (level--) {
for (int k = q.size(); k; --k) {
int i = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int j : friends[i]) {
if (!vis[j]) {
vis[j] = true;
q.push(j);
}
}
}
}
unordered_map<string, int> cnt;
while (!q.empty()) {
int i = q.front();
q.pop();
for (const auto& v : watchedVideos[i]) {
cnt[v]++;
}
}
vector<string> ans;
for (const auto& [key, _] : cnt) {
ans.push_back(key);
}
sort(ans.begin(), ans.end(), [&cnt](const string& a, const string& b) {
return cnt[a] == cnt[b] ? a < b : cnt[a] < cnt[b];
});
return ans;
}
};func watchedVideosByFriends(watchedVideos [][]string, friends [][]int, id int, level int) []string {
q := []int{id}
n := len(friends)
vis := make([]bool, n)
vis[id] = true
for level > 0 {
level--
nextQ := []int{}
for _, i := range q {
for _, j := range friends[i] {
if !vis[j] {
vis[j] = true
nextQ = append(nextQ, j)
}
}
}
q = nextQ
}
cnt := make(map[string]int)
for _, i := range q {
for _, v := range watchedVideos[i] {
cnt[v]++
}
}
ans := []string{}
for key := range cnt {
ans = append(ans, key)
}
sort.Slice(ans, func(i, j int) bool {
if cnt[ans[i]] == cnt[ans[j]] {
return ans[i] < ans[j]
}
return cnt[ans[i]] < cnt[ans[j]]
})
return ans
}function watchedVideosByFriends(
watchedVideos: string[][],
friends: number[][],
id: number,
level: number,
): string[] {
let q: number[] = [id];
const n: number = friends.length;
const vis: boolean[] = Array(n).fill(false);
vis[id] = true;
while (level-- > 0) {
const nq: number[] = [];
for (const i of q) {
for (const j of friends[i]) {
if (!vis[j]) {
vis[j] = true;
nq.push(j);
}
}
}
q = nq;
}
const cnt: { [key: string]: number } = {};
for (const i of q) {
for (const v of watchedVideos[i]) {
cnt[v] = (cnt[v] || 0) + 1;
}
}
const ans: string[] = Object.keys(cnt);
ans.sort((a, b) => {
if (cnt[a] === cnt[b]) {
return a.localeCompare(b);
}
return cnt[a] - cnt[b];
});
return ans;
}