| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
1387 |
Biweekly Contest 16 Q3 |
|
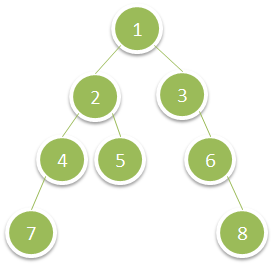
Given the root of a binary tree, return the sum of values of its deepest leaves.
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,6,7,null,null,null,null,8] Output: 15
Example 2:
Input: root = [6,7,8,2,7,1,3,9,null,1,4,null,null,null,5] Output: 19
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 104]. 1 <= Node.val <= 100
We can use breadth-first search (BFS) to traverse the binary tree level by level, and calculate the sum of the node values at each level. After completing the traversal, return the sum of the node values at the last level.
The time complexity is
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def deepestLeavesSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
q = deque([root])
while q:
ans = 0
for _ in range(len(q)):
node = q.popleft()
ans += node.val
if node.left:
q.append(node.left)
if node.right:
q.append(node.right)
return ans/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int deepestLeavesSum(TreeNode root) {
Deque<TreeNode> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
q.offer(root);
int ans = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
ans = 0;
for (int k = q.size(); k > 0; --k) {
TreeNode node = q.poll();
ans += node.val;
if (node.left != null) {
q.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
q.offer(node.right);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int deepestLeavesSum(TreeNode* root) {
int ans = 0;
queue<TreeNode*> q{{root}};
while (!q.empty()) {
ans = 0;
for (int k = q.size(); k; --k) {
TreeNode* node = q.front();
q.pop();
ans += node->val;
if (node->left) {
q.push(node->left);
}
if (node->right) {
q.push(node->right);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func deepestLeavesSum(root *TreeNode) (ans int) {
q := []*TreeNode{root}
for len(q) > 0 {
ans = 0
for k := len(q); k > 0; k-- {
node := q[0]
q = q[1:]
ans += node.Val
if node.Left != nil {
q = append(q, node.Left)
}
if node.Right != nil {
q = append(q, node.Right)
}
}
}
return
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function deepestLeavesSum(root: TreeNode | null): number {
let q: TreeNode[] = [root];
let ans = 0;
while (q.length) {
const nq: TreeNode[] = [];
ans = 0;
for (const { val, left, right } of q) {
ans += val;
left && nq.push(left);
right && nq.push(right);
}
q = nq;
}
return ans;
}// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std::rc::Rc;
use std::cell::RefCell;
use std::collections::VecDeque;
impl Solution {
pub fn deepest_leaves_sum(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> i32 {
let mut q = VecDeque::new();
q.push_back(root);
let mut ans = 0;
while !q.is_empty() {
ans = 0;
for _ in 0..q.len() {
if let Some(Some(node)) = q.pop_front() {
let node = node.borrow();
ans += node.val;
if node.left.is_some() {
q.push_back(node.left.clone());
}
if node.right.is_some() {
q.push_back(node.right.clone());
}
}
}
}
ans
}
}We can use depth-first search (DFS) to recursively traverse the binary tree while keeping track of the current node's depth, the maximum depth, and the sum of the deepest leaf nodes. When visiting the current node, if the current node's depth equals the maximum depth, add the current node's value to the sum of the deepest leaf nodes. If the current node's depth is greater than the maximum depth, update the maximum depth to the current node's depth and update the sum of the deepest leaf nodes to the current node's value.
The time complexity is
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def deepestLeavesSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
def dfs(root, i):
nonlocal ans, mx
if root is None:
return
if i == mx:
ans += root.val
elif i > mx:
ans = root.val
mx = i
dfs(root.left, i + 1)
dfs(root.right, i + 1)
ans = mx = 0
dfs(root, 1)
return ans/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int mx;
int ans;
public int deepestLeavesSum(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root, 1);
return ans;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, int i) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
if (i > mx) {
mx = i;
ans = root.val;
} else if (i == mx) {
ans += root.val;
}
dfs(root.left, i + 1);
dfs(root.right, i + 1);
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int deepestLeavesSum(TreeNode* root) {
int mx = 0, ans = 0;
auto dfs = [&](this auto&& dfs, TreeNode* root, int i) {
if (!root) {
return;
}
if (i == mx) {
ans += root->val;
} else if (i > mx) {
mx = i;
ans = root->val;
}
dfs(root->left, i + 1);
dfs(root->right, i + 1);
};
dfs(root, 1);
return ans;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func deepestLeavesSum(root *TreeNode) int {
ans, mx := 0, 0
var dfs func(*TreeNode, int)
dfs = func(root *TreeNode, i int) {
if root == nil {
return
}
if i == mx {
ans += root.Val
} else if i > mx {
mx = i
ans = root.Val
}
dfs(root.Left, i+1)
dfs(root.Right, i+1)
}
dfs(root, 1)
return ans
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function deepestLeavesSum(root: TreeNode | null): number {
let [ans, mx] = [0, 0];
const dfs = (root: TreeNode | null, i: number) => {
if (!root) {
return;
}
if (i > mx) {
mx = i;
ans = root.val;
} else if (i === mx) {
ans += root.val;
}
dfs(root.left, i + 1);
dfs(root.right, i + 1);
};
dfs(root, 1);
return ans;
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
void dfs(struct TreeNode* root, int depth, int* maxDepth, int* res) {
if (!root->left && !root->right) {
if (depth == *maxDepth) {
*res += root->val;
} else if (depth > *maxDepth) {
*maxDepth = depth;
*res = root->val;
}
return;
}
if (root->left) {
dfs(root->left, depth + 1, maxDepth, res);
}
if (root->right) {
dfs(root->right, depth + 1, maxDepth, res);
}
}
int deepestLeavesSum(struct TreeNode* root) {
int res = 0;
int maxDepth = 0;
dfs(root, 0, &maxDepth, &res);
return res;
}