| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
1732 |
Biweekly Contest 14 Q3 |
|
A tree rooted at node 0 is given as follows:
- The number of nodes is
nodes; - The value of the
ithnode isvalue[i]; - The parent of the
ithnode isparent[i].
Remove every subtree whose sum of values of nodes is zero.
Return the number of the remaining nodes in the tree.
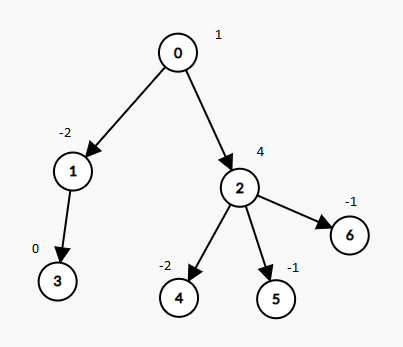
Example 1:
Input: nodes = 7, parent = [-1,0,0,1,2,2,2], value = [1,-2,4,0,-2,-1,-1] Output: 2
Example 2:
Input: nodes = 7, parent = [-1,0,0,1,2,2,2], value = [1,-2,4,0,-2,-1,-2] Output: 6
Constraints:
1 <= nodes <= 104parent.length == nodes0 <= parent[i] <= nodes - 1parent[0] == -1which indicates that0is the root.value.length == nodes-105 <= value[i] <= 105- The given input is guaranteed to represent a valid tree.
First, we convert the tree into a graph
Then we design a function
In this function, we recursively calculate the number of nodes and the sum of the weights in the subtree rooted at each child node
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def deleteTreeNodes(self, nodes: int, parent: List[int], value: List[int]) -> int:
def dfs(i):
s, m = value[i], 1
for j in g[i]:
t, n = dfs(j)
s += t
m += n
if s == 0:
m = 0
return (s, m)
g = defaultdict(list)
for i in range(1, nodes):
g[parent[i]].append(i)
return dfs(0)[1]class Solution {
private List<Integer>[] g;
private int[] value;
public int deleteTreeNodes(int nodes, int[] parent, int[] value) {
g = new List[nodes];
Arrays.setAll(g, k -> new ArrayList<>());
for (int i = 1; i < nodes; ++i) {
g[parent[i]].add(i);
}
this.value = value;
return dfs(0)[1];
}
private int[] dfs(int i) {
int[] res = new int[] {value[i], 1};
for (int j : g[i]) {
int[] t = dfs(j);
res[0] += t[0];
res[1] += t[1];
}
if (res[0] == 0) {
res[1] = 0;
}
return res;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int deleteTreeNodes(int nodes, vector<int>& parent, vector<int>& value) {
vector<vector<int>> g(nodes);
for (int i = 1; i < nodes; ++i) {
g[parent[i]].emplace_back(i);
}
function<pair<int, int>(int)> dfs = [&](int i) -> pair<int, int> {
int s = value[i], m = 1;
for (int j : g[i]) {
auto [t, n] = dfs(j);
s += t;
m += n;
}
if (s == 0) {
m = 0;
}
return pair<int, int>{s, m};
};
return dfs(0).second;
}
};func deleteTreeNodes(nodes int, parent []int, value []int) int {
g := make([][]int, nodes)
for i := 1; i < nodes; i++ {
g[parent[i]] = append(g[parent[i]], i)
}
type pair struct{ s, n int }
var dfs func(int) pair
dfs = func(i int) pair {
s, m := value[i], 1
for _, j := range g[i] {
t := dfs(j)
s += t.s
m += t.n
}
if s == 0 {
m = 0
}
return pair{s, m}
}
return dfs(0).n
}