| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
1570 |
Weekly Contest 130 Q3 |
|
You are given the head of a linked list with n nodes.
For each node in the list, find the value of the next greater node. That is, for each node, find the value of the first node that is next to it and has a strictly larger value than it.
Return an integer array answer where answer[i] is the value of the next greater node of the ith node (1-indexed). If the ith node does not have a next greater node, set answer[i] = 0.
Example 1:
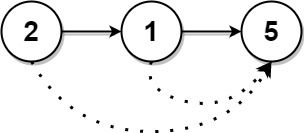
Input: head = [2,1,5] Output: [5,5,0]
Example 2:
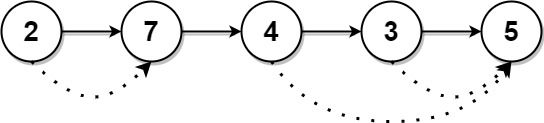
Input: head = [2,7,4,3,5] Output: [7,0,5,5,0]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is
n. 1 <= n <= 1041 <= Node.val <= 109
The problem requires finding the next larger node for each node in the linked list, that is, finding the first node to the right of each node in the linked list that is larger than it. We first traverse the linked list and store the values in the linked list in an array
We traverse the array
If the stack is empty at this time, it means that the current element does not have a next larger element, otherwise, the next larger element of the current element is the top element of the stack, and we update the answer array
After the traversal is over, we return the answer array
The time complexity is
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def nextLargerNodes(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> List[int]:
nums = []
while head:
nums.append(head.val)
head = head.next
stk = []
n = len(nums)
ans = [0] * n
for i in range(n - 1, -1, -1):
while stk and stk[-1] <= nums[i]:
stk.pop()
if stk:
ans[i] = stk[-1]
stk.append(nums[i])
return ans/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int[] nextLargerNodes(ListNode head) {
List<Integer> nums = new ArrayList<>();
for (; head != null; head = head.next) {
nums.add(head.val);
}
Deque<Integer> stk = new ArrayDeque<>();
int n = nums.size();
int[] ans = new int[n];
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
while (!stk.isEmpty() && stk.peek() <= nums.get(i)) {
stk.pop();
}
if (!stk.isEmpty()) {
ans[i] = stk.peek();
}
stk.push(nums.get(i));
}
return ans;
}
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> nextLargerNodes(ListNode* head) {
vector<int> nums;
for (; head; head = head->next) {
nums.push_back(head->val);
}
stack<int> stk;
int n = nums.size();
vector<int> ans(n);
for (int i = n - 1; ~i; --i) {
while (!stk.empty() && stk.top() <= nums[i]) {
stk.pop();
}
if (!stk.empty()) {
ans[i] = stk.top();
}
stk.push(nums[i]);
}
return ans;
}
};/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func nextLargerNodes(head *ListNode) []int {
nums := []int{}
for ; head != nil; head = head.Next {
nums = append(nums, head.Val)
}
stk := []int{}
n := len(nums)
ans := make([]int, n)
for i := n - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
for len(stk) > 0 && stk[len(stk)-1] <= nums[i] {
stk = stk[:len(stk)-1]
}
if len(stk) > 0 {
ans[i] = stk[len(stk)-1]
}
stk = append(stk, nums[i])
}
return ans
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* val: number
* next: ListNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
* }
*/
function nextLargerNodes(head: ListNode | null): number[] {
const nums: number[] = [];
while (head) {
nums.push(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
const stk: number[] = [];
const n = nums.length;
const ans: number[] = Array(n).fill(0);
for (let i = n - 1; ~i; --i) {
while (stk.length && stk.at(-1)! <= nums[i]) {
stk.pop();
}
ans[i] = stk.length ? stk.at(-1)! : 0;
stk.push(nums[i]);
}
return ans;
}// Definition for singly-linked list.
// #[derive(PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Debug)]
// pub struct ListNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>>
// }
//
// impl ListNode {
// #[inline]
// fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// ListNode {
// next: None,
// val
// }
// }
// }
use std::collections::VecDeque;
impl Solution {
pub fn next_larger_nodes(head: Option<Box<ListNode>>) -> Vec<i32> {
let mut nums = Vec::new();
let mut current = &head;
while let Some(node) = current {
nums.push(node.val);
current = &node.next;
}
let mut stk = VecDeque::new();
let n = nums.len();
let mut ans = vec![0; n];
for i in (0..n).rev() {
while !stk.is_empty() && stk.back().copied().unwrap() <= nums[i] {
stk.pop_back();
}
if let Some(&top) = stk.back() {
ans[i] = top;
}
stk.push_back(nums[i]);
}
ans
}
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {number[]}
*/
var nextLargerNodes = function (head) {
const nums = [];
while (head) {
nums.push(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
const stk = [];
const n = nums.length;
const ans = new Array(n).fill(0);
for (let i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
while (stk.length && stk[stk.length - 1] <= nums[i]) {
stk.pop();
}
ans[i] = stk.length ? stk[stk.length - 1] : 0;
stk.push(nums[i]);
}
return ans;
};