| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Hard |
|
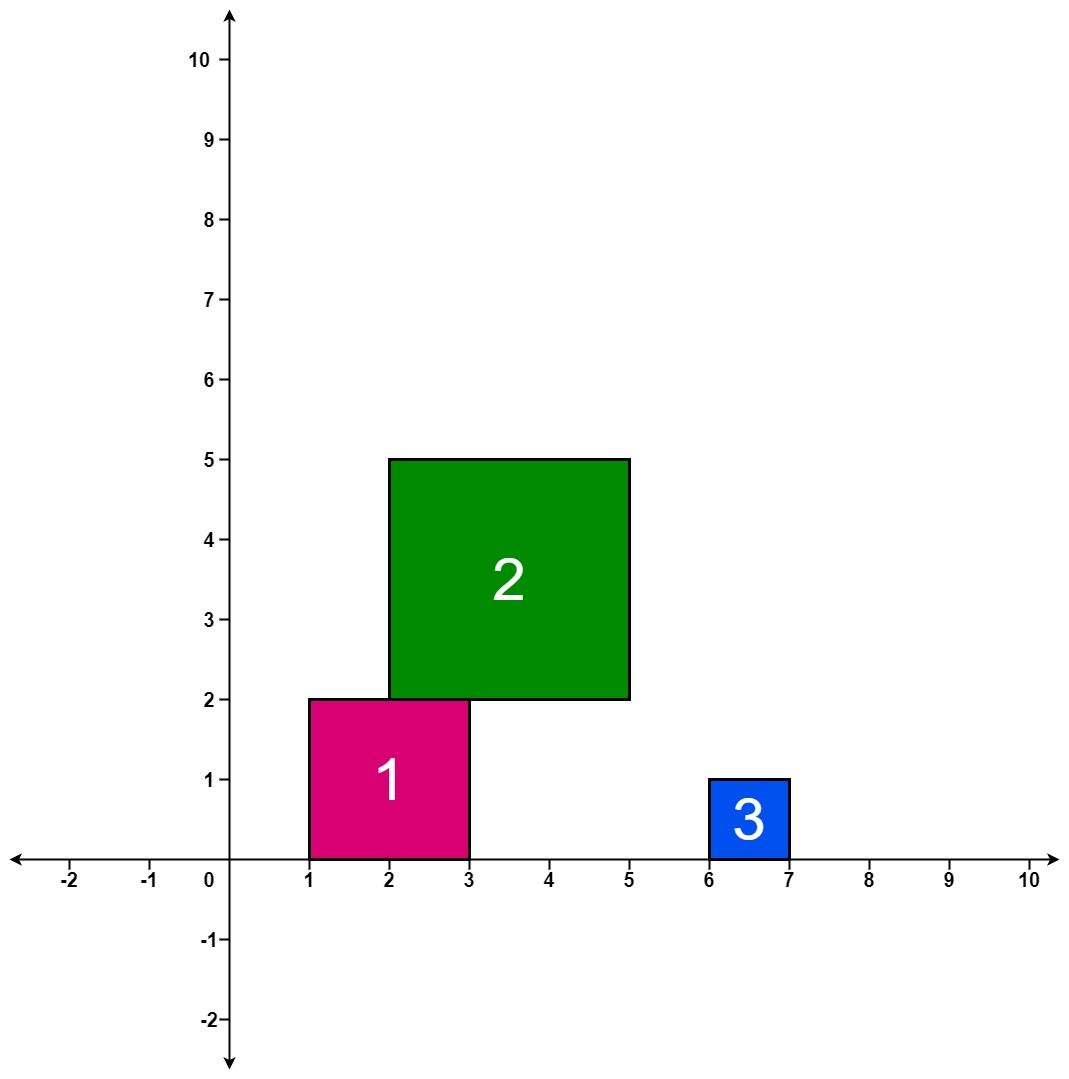
There are several squares being dropped onto the X-axis of a 2D plane.
You are given a 2D integer array positions where positions[i] = [lefti, sideLengthi] represents the ith square with a side length of sideLengthi that is dropped with its left edge aligned with X-coordinate lefti.
Each square is dropped one at a time from a height above any landed squares. It then falls downward (negative Y direction) until it either lands on the top side of another square or on the X-axis. A square brushing the left/right side of another square does not count as landing on it. Once it lands, it freezes in place and cannot be moved.
After each square is dropped, you must record the height of the current tallest stack of squares.
Return an integer array ans where ans[i] represents the height described above after dropping the ith square.
Example 1:
Input: positions = [[1,2],[2,3],[6,1]] Output: [2,5,5] Explanation: After the first drop, the tallest stack is square 1 with a height of 2. After the second drop, the tallest stack is squares 1 and 2 with a height of 5. After the third drop, the tallest stack is still squares 1 and 2 with a height of 5. Thus, we return an answer of [2, 5, 5].
Example 2:
Input: positions = [[100,100],[200,100]] Output: [100,100] Explanation: After the first drop, the tallest stack is square 1 with a height of 100. After the second drop, the tallest stack is either square 1 or square 2, both with heights of 100. Thus, we return an answer of [100, 100]. Note that square 2 only brushes the right side of square 1, which does not count as landing on it.
Constraints:
1 <= positions.length <= 10001 <= lefti <= 1081 <= sideLengthi <= 106
According to the problem description, we need to maintain a set of intervals that support modification and query operations. In this case, we can use a segment tree to solve the problem.
A segment tree divides the entire interval into multiple non-contiguous sub-intervals, with the number of sub-intervals not exceeding
- Each node of the segment tree represents an interval;
- The segment tree has a unique root node representing the entire statistical range, such as
$[1, n]$ ; - Each leaf node of the segment tree represents a primitive interval of length 1,
$[x, x]$ ; - For each internal node
$[l, r]$ , its left child is$[l, \textit{mid}]$ , and its right child is$[\textit{mid} + 1, r]$ , where$\textit{mid} = \frac{l + r}{2}$ ;
For this problem, the information maintained by the segment tree nodes includes:
- The maximum height
$v$ of the blocks in the interval - Lazy propagation marker
$add$
Additionally, since the range of the number line is very large, up to
In terms of time complexity, each query and modification has a time complexity of
class Node:
def __init__(self, l, r):
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.l = l
self.r = r
self.mid = (l + r) >> 1
self.v = 0
self.add = 0
class SegmentTree:
def __init__(self):
self.root = Node(1, int(1e9))
def modify(self, l, r, v, node=None):
if l > r:
return
if node is None:
node = self.root
if node.l >= l and node.r <= r:
node.v = v
node.add = v
return
self.pushdown(node)
if l <= node.mid:
self.modify(l, r, v, node.left)
if r > node.mid:
self.modify(l, r, v, node.right)
self.pushup(node)
def query(self, l, r, node=None):
if l > r:
return 0
if node is None:
node = self.root
if node.l >= l and node.r <= r:
return node.v
self.pushdown(node)
v = 0
if l <= node.mid:
v = max(v, self.query(l, r, node.left))
if r > node.mid:
v = max(v, self.query(l, r, node.right))
return v
def pushup(self, node):
node.v = max(node.left.v, node.right.v)
def pushdown(self, node):
if node.left is None:
node.left = Node(node.l, node.mid)
if node.right is None:
node.right = Node(node.mid + 1, node.r)
if node.add:
node.left.v = node.add
node.right.v = node.add
node.left.add = node.add
node.right.add = node.add
node.add = 0
class Solution:
def fallingSquares(self, positions: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
ans = []
mx = 0
tree = SegmentTree()
for l, w in positions:
r = l + w - 1
h = tree.query(l, r) + w
mx = max(mx, h)
ans.append(mx)
tree.modify(l, r, h)
return ansclass Node {
Node left;
Node right;
int l;
int r;
int mid;
int v;
int add;
public Node(int l, int r) {
this.l = l;
this.r = r;
this.mid = (l + r) >> 1;
}
}
class SegmentTree {
private Node root = new Node(1, (int) 1e9);
public SegmentTree() {
}
public void modify(int l, int r, int v) {
modify(l, r, v, root);
}
public void modify(int l, int r, int v, Node node) {
if (l > r) {
return;
}
if (node.l >= l && node.r <= r) {
node.v = v;
node.add = v;
return;
}
pushdown(node);
if (l <= node.mid) {
modify(l, r, v, node.left);
}
if (r > node.mid) {
modify(l, r, v, node.right);
}
pushup(node);
}
public int query(int l, int r) {
return query(l, r, root);
}
public int query(int l, int r, Node node) {
if (l > r) {
return 0;
}
if (node.l >= l && node.r <= r) {
return node.v;
}
pushdown(node);
int v = 0;
if (l <= node.mid) {
v = Math.max(v, query(l, r, node.left));
}
if (r > node.mid) {
v = Math.max(v, query(l, r, node.right));
}
return v;
}
public void pushup(Node node) {
node.v = Math.max(node.left.v, node.right.v);
}
public void pushdown(Node node) {
if (node.left == null) {
node.left = new Node(node.l, node.mid);
}
if (node.right == null) {
node.right = new Node(node.mid + 1, node.r);
}
if (node.add != 0) {
Node left = node.left, right = node.right;
left.add = node.add;
right.add = node.add;
left.v = node.add;
right.v = node.add;
node.add = 0;
}
}
}
class Solution {
public List<Integer> fallingSquares(int[][] positions) {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
SegmentTree tree = new SegmentTree();
int mx = 0;
for (int[] p : positions) {
int l = p[0], w = p[1], r = l + w - 1;
int h = tree.query(l, r) + w;
mx = Math.max(mx, h);
ans.add(mx);
tree.modify(l, r, h);
}
return ans;
}
}class Node {
public:
Node* left;
Node* right;
int l;
int r;
int mid;
int v;
int add;
Node(int l, int r) {
this->l = l;
this->r = r;
this->mid = (l + r) >> 1;
this->left = this->right = nullptr;
v = add = 0;
}
};
class SegmentTree {
private:
Node* root;
public:
SegmentTree() {
root = new Node(1, 1e9);
}
void modify(int l, int r, int v) {
modify(l, r, v, root);
}
void modify(int l, int r, int v, Node* node) {
if (l > r) return;
if (node->l >= l && node->r <= r) {
node->v = v;
node->add = v;
return;
}
pushdown(node);
if (l <= node->mid) modify(l, r, v, node->left);
if (r > node->mid) modify(l, r, v, node->right);
pushup(node);
}
int query(int l, int r) {
return query(l, r, root);
}
int query(int l, int r, Node* node) {
if (l > r) return 0;
if (node->l >= l && node->r <= r) return node->v;
pushdown(node);
int v = 0;
if (l <= node->mid) v = max(v, query(l, r, node->left));
if (r > node->mid) v = max(v, query(l, r, node->right));
return v;
}
void pushup(Node* node) {
node->v = max(node->left->v, node->right->v);
}
void pushdown(Node* node) {
if (!node->left) node->left = new Node(node->l, node->mid);
if (!node->right) node->right = new Node(node->mid + 1, node->r);
if (node->add) {
Node* left = node->left;
Node* right = node->right;
left->v = node->add;
right->v = node->add;
left->add = node->add;
right->add = node->add;
node->add = 0;
}
}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> fallingSquares(vector<vector<int>>& positions) {
vector<int> ans;
SegmentTree* tree = new SegmentTree();
int mx = 0;
for (auto& p : positions) {
int l = p[0], w = p[1], r = l + w - 1;
int h = tree->query(l, r) + w;
mx = max(mx, h);
ans.push_back(mx);
tree->modify(l, r, h);
}
return ans;
}
};type node struct {
left *node
right *node
l, mid, r int
v, add int
}
func newNode(l, r int) *node {
return &node{
l: l,
r: r,
mid: (l + r) >> 1,
}
}
type segmentTree struct {
root *node
}
func newSegmentTree() *segmentTree {
return &segmentTree{
root: newNode(1, 1e9),
}
}
func (t *segmentTree) modify(l, r, v int, n *node) {
if l > r {
return
}
if n.l >= l && n.r <= r {
n.v = v
n.add = v
return
}
t.pushdown(n)
if l <= n.mid {
t.modify(l, r, v, n.left)
}
if r > n.mid {
t.modify(l, r, v, n.right)
}
t.pushup(n)
}
func (t *segmentTree) query(l, r int, n *node) int {
if l > r {
return 0
}
if n.l >= l && n.r <= r {
return n.v
}
t.pushdown(n)
v := 0
if l <= n.mid {
v = max(v, t.query(l, r, n.left))
}
if r > n.mid {
v = max(v, t.query(l, r, n.right))
}
return v
}
func (t *segmentTree) pushup(n *node) {
n.v = max(n.left.v, n.right.v)
}
func (t *segmentTree) pushdown(n *node) {
if n.left == nil {
n.left = newNode(n.l, n.mid)
}
if n.right == nil {
n.right = newNode(n.mid+1, n.r)
}
if n.add != 0 {
n.left.add = n.add
n.right.add = n.add
n.left.v = n.add
n.right.v = n.add
n.add = 0
}
}
func fallingSquares(positions [][]int) []int {
ans := make([]int, len(positions))
t := newSegmentTree()
mx := 0
for i, p := range positions {
l, w, r := p[0], p[1], p[0]+p[1]-1
h := t.query(l, r, t.root) + w
mx = max(mx, h)
ans[i] = mx
t.modify(l, r, h, t.root)
}
return ans
}class Node {
left: Node | null = null;
right: Node | null = null;
l: number;
r: number;
mid: number;
v: number = 0;
add: number = 0;
constructor(l: number, r: number) {
this.l = l;
this.r = r;
this.mid = (l + r) >> 1;
}
}
class SegmentTree {
private root: Node = new Node(1, 1e9);
public modify(l: number, r: number, v: number): void {
this.modifyNode(l, r, v, this.root);
}
private modifyNode(l: number, r: number, v: number, node: Node): void {
if (l > r) {
return;
}
if (node.l >= l && node.r <= r) {
node.v = v;
node.add = v;
return;
}
this.pushdown(node);
if (l <= node.mid) {
this.modifyNode(l, r, v, node.left!);
}
if (r > node.mid) {
this.modifyNode(l, r, v, node.right!);
}
this.pushup(node);
}
public query(l: number, r: number): number {
return this.queryNode(l, r, this.root);
}
private queryNode(l: number, r: number, node: Node): number {
if (l > r) {
return 0;
}
if (node.l >= l && node.r <= r) {
return node.v;
}
this.pushdown(node);
let v = 0;
if (l <= node.mid) {
v = Math.max(v, this.queryNode(l, r, node.left!));
}
if (r > node.mid) {
v = Math.max(v, this.queryNode(l, r, node.right!));
}
return v;
}
private pushup(node: Node): void {
node.v = Math.max(node.left!.v, node.right!.v);
}
private pushdown(node: Node): void {
if (node.left == null) {
node.left = new Node(node.l, node.mid);
}
if (node.right == null) {
node.right = new Node(node.mid + 1, node.r);
}
if (node.add != 0) {
let left = node.left,
right = node.right;
left!.add = node.add;
right!.add = node.add;
left!.v = node.add;
right!.v = node.add;
node.add = 0;
}
}
}
function fallingSquares(positions: number[][]): number[] {
const ans: number[] = [];
const tree = new SegmentTree();
let mx = 0;
for (const [l, w] of positions) {
const r = l + w - 1;
const h = tree.query(l, r) + w;
mx = Math.max(mx, h);
ans.push(mx);
tree.modify(l, r, h);
}
return ans;
}