| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
中等 |
|
给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,和一个整数 targetSum ,求该二叉树里节点值之和等于 targetSum 的 路径 的数目。
路径 不需要从根节点开始,也不需要在叶子节点结束,但是路径方向必须是向下的(只能从父节点到子节点)。
示例 1:
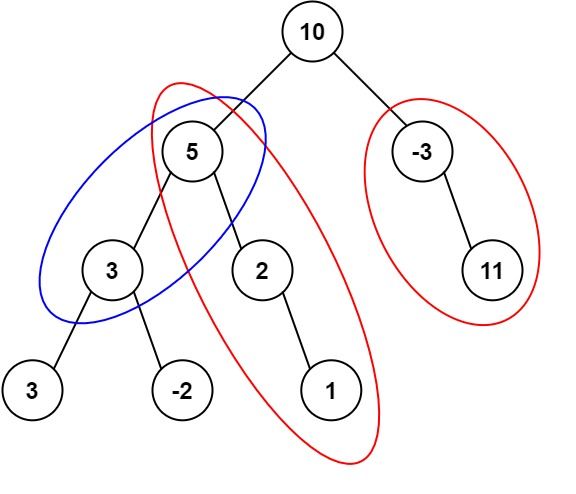
输入:root = [10,5,-3,3,2,null,11,3,-2,null,1], targetSum = 8 输出:3 解释:和等于 8 的路径有 3 条,如图所示。
示例 2:
输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22 输出:3
提示:
- 二叉树的节点个数的范围是
[0,1000] -109 <= Node.val <= 109-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
我们可以运用前缀和的思想,对二叉树进行递归遍历,同时用哈希表
我们设计一个递归函数
函数
- 如果当前节点
$node$ 为空,则返回$0$ 。 - 计算从根节点到当前节点的路径上的前缀和
$s$ 。 - 用
$cnt[s - targetSum]$ 表示以当前节点为路径终点且路径和为$targetSum$ 的路径数目,其中$cnt[s - targetSum]$ 即为$cnt$ 中前缀和为$s - targetSum$ 的个数。 - 将前缀和
$s$ 的计数值加$1$ ,即$cnt[s] = cnt[s] + 1$ 。 - 递归地遍历当前节点的左右子节点,即调用函数
$dfs(node.left, s)$ 和$dfs(node.right, s)$ ,并将它们的返回值相加。 - 在返回值计算完成以后,需要将当前节点的前缀和
$s$ 的计数值减$1$ ,即执行$cnt[s] = cnt[s] - 1$ 。 - 最后返回答案。
时间复杂度
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def pathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> int:
def dfs(node, s):
if node is None:
return 0
s += node.val
ans = cnt[s - targetSum]
cnt[s] += 1
ans += dfs(node.left, s)
ans += dfs(node.right, s)
cnt[s] -= 1
return ans
cnt = Counter({0: 1})
return dfs(root, 0)/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private Map<Long, Integer> cnt = new HashMap<>();
private int targetSum;
public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
cnt.put(0L, 1);
this.targetSum = targetSum;
return dfs(root, 0);
}
private int dfs(TreeNode node, long s) {
if (node == null) {
return 0;
}
s += node.val;
int ans = cnt.getOrDefault(s - targetSum, 0);
cnt.merge(s, 1, Integer::sum);
ans += dfs(node.left, s);
ans += dfs(node.right, s);
cnt.merge(s, -1, Integer::sum);
return ans;
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
unordered_map<long, int> cnt;
cnt[0] = 1;
function<int(TreeNode*, long)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* node, long s) -> int {
if (!node) return 0;
s += node->val;
int ans = cnt[s - targetSum];
++cnt[s];
ans += dfs(node->left, s) + dfs(node->right, s);
--cnt[s];
return ans;
};
return dfs(root, 0);
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func pathSum(root *TreeNode, targetSum int) int {
cnt := map[int]int{0: 1}
var dfs func(*TreeNode, int) int
dfs = func(node *TreeNode, s int) int {
if node == nil {
return 0
}
s += node.Val
ans := cnt[s-targetSum]
cnt[s]++
ans += dfs(node.Left, s) + dfs(node.Right, s)
cnt[s]--
return ans
}
return dfs(root, 0)
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function pathSum(root: TreeNode | null, targetSum: number): number {
const cnt: Map<number, number> = new Map();
const dfs = (node: TreeNode | null, s: number): number => {
if (!node) {
return 0;
}
s += node.val;
let ans = cnt.get(s - targetSum) ?? 0;
cnt.set(s, (cnt.get(s) ?? 0) + 1);
ans += dfs(node.left, s);
ans += dfs(node.right, s);
cnt.set(s, (cnt.get(s) ?? 0) - 1);
return ans;
};
cnt.set(0, 1);
return dfs(root, 0);
}