| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Easy |
|
Given the root of a binary tree, return the sum of all left leaves.
A leaf is a node with no children. A left leaf is a leaf that is the left child of another node.
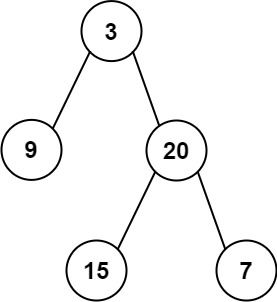
Example 1:
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: 24 Explanation: There are two left leaves in the binary tree, with values 9 and 15 respectively.
Example 2:
Input: root = [1] Output: 0
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 1000]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
First, we check if root is null. If it is, we return
Otherwise, we recursively call the sumOfLeftLeaves function to calculate the sum of all left leaves in root's right subtree, and assign the result to the answer variable root's left child exists. If it does, we check if it is a leaf node. If it is a leaf node, we add its value to the answer variable sumOfLeftLeaves function to calculate the sum of all left leaves in root's left subtree, and add the result to the answer variable
Finally, we return the answer.
The time complexity is
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def sumOfLeftLeaves(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
if root is None:
return 0
ans = self.sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right)
if root.left:
if root.left.left == root.left.right:
ans += root.left.val
else:
ans += self.sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left)
return ans/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int ans = sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right);
if (root.left != null) {
if (root.left.left == root.left.right) {
ans += root.left.val;
} else {
ans += sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left);
}
}
return ans;
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) {
return 0;
}
int ans = sumOfLeftLeaves(root->right);
if (root->left) {
if (!root->left->left && !root->left->right) {
ans += root->left->val;
} else {
ans += sumOfLeftLeaves(root->left);
}
}
return ans;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func sumOfLeftLeaves(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
ans := sumOfLeftLeaves(root.Right)
if root.Left != nil {
if root.Left.Left == root.Left.Right {
ans += root.Left.Val
} else {
ans += sumOfLeftLeaves(root.Left)
}
}
return ans
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function sumOfLeftLeaves(root: TreeNode | null): number {
if (!root) {
return 0;
}
let ans = sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right);
if (root.left) {
if (root.left.left === root.left.right) {
ans += root.left.val;
} else {
ans += sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left);
}
}
return ans;
}// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std::cell::RefCell;
use std::rc::Rc;
impl Solution {
fn dfs(root: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, is_left: bool) -> i32 {
if root.is_none() {
return 0;
}
let node = root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow();
let left = &node.left;
let right = &node.right;
if left.is_none() && right.is_none() {
if is_left {
return node.val;
}
return 0;
}
Self::dfs(left, true) + Self::dfs(right, false)
}
pub fn sum_of_left_leaves(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> i32 {
Self::dfs(&root, false)
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
int sumOfLeftLeaves(struct TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) {
return 0;
}
int ans = sumOfLeftLeaves(root->right);
if (root->left) {
if (!root->left->left && !root->left->right) {
ans += root->left->val;
} else {
ans += sumOfLeftLeaves(root->left);
}
}
return ans;
}We can also convert the recursion in Solution 1 to iteration, using a stack to simulate the recursion process.
Similar to Solution 1, we first check if root is null. If it is, we return
Otherwise, we initialize the answer variable root to the stack.
While the stack is not empty, we pop the top element root from the stack. If root's left child exists, we check if it is a leaf node. If it is a leaf node, we add its value to the answer variable root's right child exists. If it does, we add it to the stack.
Finally, we return the answer.
The time complexity is
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def sumOfLeftLeaves(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
if root is None:
return 0
ans = 0
stk = [root]
while stk:
root = stk.pop()
if root.left:
if root.left.left == root.left.right:
ans += root.left.val
else:
stk.append(root.left)
if root.right:
stk.append(root.right)
return ans/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
Deque<TreeNode> stk = new ArrayDeque<>();
stk.push(root);
int ans = 0;
while (!stk.isEmpty()) {
root = stk.pop();
if (root.left != null) {
if (root.left.left == root.left.right) {
ans += root.left.val;
} else {
stk.push(root.left);
}
}
if (root.right != null) {
stk.push(root.right);
}
}
return ans;
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) {
return 0;
}
int ans = 0;
stack<TreeNode*> stk{{root}};
while (!stk.empty()) {
root = stk.top(), stk.pop();
if (root->left) {
if (!root->left->left && !root->left->right) {
ans += root->left->val;
} else {
stk.push(root->left);
}
}
if (root->right) {
stk.push(root->right);
}
}
return ans;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func sumOfLeftLeaves(root *TreeNode) (ans int) {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
stk := []*TreeNode{root}
for len(stk) > 0 {
root = stk[len(stk)-1]
stk = stk[:len(stk)-1]
if root.Left != nil {
if root.Left.Left == root.Left.Right {
ans += root.Left.Val
} else {
stk = append(stk, root.Left)
}
}
if root.Right != nil {
stk = append(stk, root.Right)
}
}
return
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function sumOfLeftLeaves(root: TreeNode | null): number {
if (!root) {
return 0;
}
let ans = 0;
const stk: TreeNode[] = [root];
while (stk.length) {
const { left, right } = stk.pop()!;
if (left) {
if (left.left === left.right) {
ans += left.val;
} else {
stk.push(left);
}
}
if (right) {
stk.push(right);
}
}
return ans;
}