| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Hard |
|
A city's skyline is the outer contour of the silhouette formed by all the buildings in that city when viewed from a distance. Given the locations and heights of all the buildings, return the skyline formed by these buildings collectively.
The geometric information of each building is given in the array buildings where buildings[i] = [lefti, righti, heighti]:
leftiis the x coordinate of the left edge of theithbuilding.rightiis the x coordinate of the right edge of theithbuilding.heightiis the height of theithbuilding.
You may assume all buildings are perfect rectangles grounded on an absolutely flat surface at height 0.
The skyline should be represented as a list of "key points" sorted by their x-coordinate in the form [[x1,y1],[x2,y2],...]. Each key point is the left endpoint of some horizontal segment in the skyline except the last point in the list, which always has a y-coordinate 0 and is used to mark the skyline's termination where the rightmost building ends. Any ground between the leftmost and rightmost buildings should be part of the skyline's contour.
Note: There must be no consecutive horizontal lines of equal height in the output skyline. For instance, [...,[2 3],[4 5],[7 5],[11 5],[12 7],...] is not acceptable; the three lines of height 5 should be merged into one in the final output as such: [...,[2 3],[4 5],[12 7],...]
Example 1:
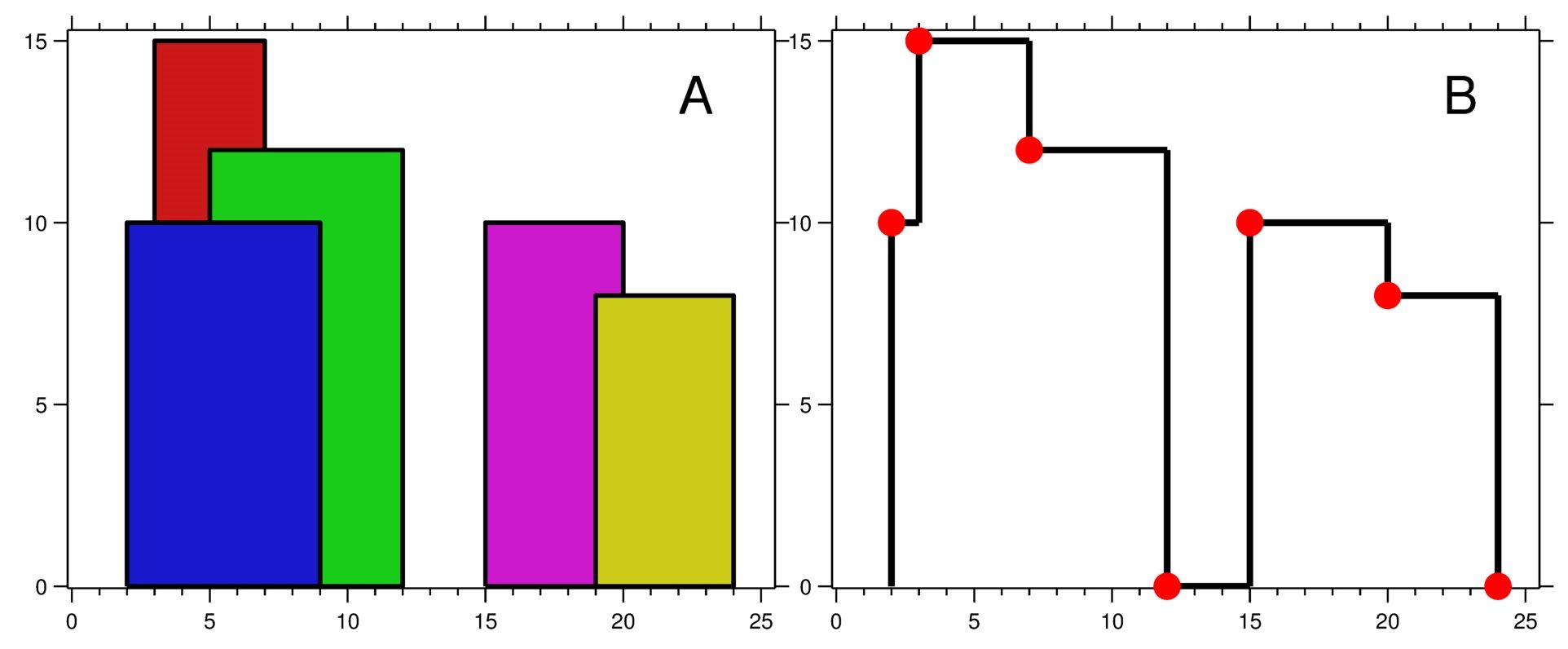
Input: buildings = [[2,9,10],[3,7,15],[5,12,12],[15,20,10],[19,24,8]] Output: [[2,10],[3,15],[7,12],[12,0],[15,10],[20,8],[24,0]] Explanation: Figure A shows the buildings of the input. Figure B shows the skyline formed by those buildings. The red points in figure B represent the key points in the output list.
Example 2:
Input: buildings = [[0,2,3],[2,5,3]] Output: [[0,3],[5,0]]
Constraints:
1 <= buildings.length <= 1040 <= lefti < righti <= 231 - 11 <= heighti <= 231 - 1buildingsis sorted byleftiin non-decreasing order.
from queue import PriorityQueue
class Solution:
def getSkyline(self, buildings: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
skys, lines, pq = [], [], PriorityQueue()
for build in buildings:
lines.extend([build[0], build[1]])
lines.sort()
city, n = 0, len(buildings)
for line in lines:
while city < n and buildings[city][0] <= line:
pq.put([-buildings[city][2], buildings[city][0], buildings[city][1]])
city += 1
while not pq.empty() and pq.queue[0][2] <= line:
pq.get()
high = 0
if not pq.empty():
high = -pq.queue[0][0]
if len(skys) > 0 and skys[-1][1] == high:
continue
skys.append([line, high])
return skysclass Solution {
public:
vector<pair<int, int>> getSkyline(vector<vector<int>>& buildings) {
set<int> poss;
map<int, int> m;
for (auto v : buildings) {
poss.insert(v[0]);
poss.insert(v[1]);
}
int i = 0;
for (int pos : poss)
m.insert(pair<int, int>(pos, i++));
vector<int> highs(m.size(), 0);
for (auto v : buildings) {
const int b = m[v[0]], e = m[v[1]];
for (int i = b; i < e; ++i)
highs[i] = max(highs[i], v[2]);
}
vector<pair<int, int>> res;
vector<int> mm(poss.begin(), poss.end());
for (int i = 0; i < highs.size(); ++i) {
if (highs[i] != highs[i + 1])
res.push_back(pair<int, int>(mm[i], highs[i]));
else {
const int start = i;
res.push_back(pair<int, int>(mm[start], highs[i]));
while (highs[i] == highs[i + 1])
++i;
}
}
return res;
}
};type Matrix struct{ left, right, height int }
type Queue []Matrix
func (q Queue) Len() int { return len(q) }
func (q Queue) Top() Matrix { return q[0] }
func (q Queue) Swap(i, j int) { q[i], q[j] = q[j], q[i] }
func (q Queue) Less(i, j int) bool { return q[i].height > q[j].height }
func (q *Queue) Push(x any) { *q = append(*q, x.(Matrix)) }
func (q *Queue) Pop() any {
old, x := *q, (*q)[len(*q)-1]
*q = old[:len(old)-1]
return x
}
func getSkyline(buildings [][]int) [][]int {
skys, lines, pq := make([][]int, 0), make([]int, 0), &Queue{}
heap.Init(pq)
for _, v := range buildings {
lines = append(lines, v[0], v[1])
}
sort.Ints(lines)
city, n := 0, len(buildings)
for _, line := range lines {
// 将所有符合条件的矩形加入队列
for ; city < n && buildings[city][0] <= line && buildings[city][1] > line; city++ {
v := Matrix{left: buildings[city][0], right: buildings[city][1], height: buildings[city][2]}
heap.Push(pq, v)
}
// 从队列移除不符合条件的矩形
for pq.Len() > 0 && pq.Top().right <= line {
heap.Pop(pq)
}
high := 0
// 队列为空说明是最右侧建筑物的终点,其轮廓点为 (line, 0)
if pq.Len() != 0 {
high = pq.Top().height
}
// 如果该点高度和前一个轮廓点一样的话,直接忽略
if len(skys) > 0 && skys[len(skys)-1][1] == high {
continue
}
skys = append(skys, []int{line, high})
}
return skys
}impl Solution {
pub fn get_skyline(buildings: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
let mut skys: Vec<Vec<i32>> = vec![];
let mut lines = vec![];
for building in buildings.iter() {
lines.push(building[0]);
lines.push(building[1]);
}
lines.sort_unstable();
let mut pq = std::collections::BinaryHeap::new();
let (mut city, n) = (0, buildings.len());
for line in lines {
while city < n && buildings[city][0] <= line && buildings[city][1] > line {
pq.push((buildings[city][2], buildings[city][1]));
city += 1;
}
while !pq.is_empty() && pq.peek().unwrap().1 <= line {
pq.pop();
}
let mut high = 0;
if !pq.is_empty() {
high = pq.peek().unwrap().0;
}
if !skys.is_empty() && skys.last().unwrap()[1] == high {
continue;
}
skys.push(vec![line, high]);
}
skys
}
}