| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
|
You are given an m x n integer matrix matrix with the following two properties:
- Each row is sorted in non-decreasing order.
- The first integer of each row is greater than the last integer of the previous row.
Given an integer target, return true if target is in matrix or false otherwise.
You must write a solution in O(log(m * n)) time complexity.
Example 1:
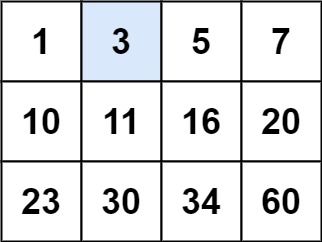
Input: matrix = [[1,3,5,7],[10,11,16,20],[23,30,34,60]], target = 3 Output: true
Example 2:
Input: matrix = [[1,3,5,7],[10,11,16,20],[23,30,34,60]], target = 13 Output: false
Constraints:
m == matrix.lengthn == matrix[i].length1 <= m, n <= 100-104 <= matrix[i][j], target <= 104
We can logically unfold the two-dimensional matrix and then perform binary search.
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def searchMatrix(self, matrix: List[List[int]], target: int) -> bool:
m, n = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
left, right = 0, m * n - 1
while left < right:
mid = (left + right) >> 1
x, y = divmod(mid, n)
if matrix[x][y] >= target:
right = mid
else:
left = mid + 1
return matrix[left // n][left % n] == targetclass Solution {
public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
int left = 0, right = m * n - 1;
while (left < right) {
int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
int x = mid / n, y = mid % n;
if (matrix[x][y] >= target) {
right = mid;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return matrix[left / n][left % n] == target;
}
}class Solution {
public:
bool searchMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int target) {
int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size();
int left = 0, right = m * n - 1;
while (left < right) {
int mid = left + right >> 1;
int x = mid / n, y = mid % n;
if (matrix[x][y] >= target) {
right = mid;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return matrix[left / n][left % n] == target;
}
};func searchMatrix(matrix [][]int, target int) bool {
m, n := len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
left, right := 0, m*n-1
for left < right {
mid := (left + right) >> 1
x, y := mid/n, mid%n
if matrix[x][y] >= target {
right = mid
} else {
left = mid + 1
}
}
return matrix[left/n][left%n] == target
}function searchMatrix(matrix: number[][], target: number): boolean {
const m = matrix.length;
const n = matrix[0].length;
let left = 0;
let right = m * n;
while (left < right) {
const mid = (left + right) >>> 1;
const i = Math.floor(mid / n);
const j = mid % n;
if (matrix[i][j] === target) {
return true;
}
if (matrix[i][j] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid;
}
}
return false;
}use std::cmp::Ordering;
impl Solution {
pub fn search_matrix(matrix: Vec<Vec<i32>>, target: i32) -> bool {
let m = matrix.len();
let n = matrix[0].len();
let mut i = 0;
let mut j = n;
while i < m && j > 0 {
match matrix[i][j - 1].cmp(&target) {
Ordering::Equal => {
return true;
}
Ordering::Less => {
i += 1;
}
Ordering::Greater => {
j -= 1;
}
}
}
false
}
}/**
* @param {number[][]} matrix
* @param {number} target
* @return {boolean}
*/
var searchMatrix = function (matrix, target) {
const m = matrix.length,
n = matrix[0].length;
let left = 0,
right = m * n - 1;
while (left < right) {
const mid = (left + right + 1) >> 1;
const x = Math.floor(mid / n);
const y = mid % n;
if (matrix[x][y] <= target) {
left = mid;
} else {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
return matrix[Math.floor(left / n)][left % n] == target;
};Here, we start searching from the bottom left corner and move towards the top right direction. We compare the current element
- If
$matrix[i][j] = target$ , we have found the target value and returntrue. - If
$matrix[i][j] > target$ , all elements to the right of the current position in this row are greater than target, so we should move the pointer$i$ upwards, i.e.,$i = i - 1$ . - If
$matrix[i][j] < target$ , all elements above the current position in this column are less than target, so we should move the pointer$j$ to the right, i.e.,$j = j + 1$ .
If we still can't find false.
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def searchMatrix(self, matrix: List[List[int]], target: int) -> bool:
m, n = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
i, j = m - 1, 0
while i >= 0 and j < n:
if matrix[i][j] == target:
return True
if matrix[i][j] > target:
i -= 1
else:
j += 1
return Falseclass Solution {
public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
for (int i = m - 1, j = 0; i >= 0 && j < n;) {
if (matrix[i][j] == target) {
return true;
}
if (matrix[i][j] > target) {
--i;
} else {
++j;
}
}
return false;
}
}class Solution {
public:
bool searchMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int target) {
int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size();
for (int i = m - 1, j = 0; i >= 0 && j < n;) {
if (matrix[i][j] == target) return true;
if (matrix[i][j] > target)
--i;
else
++j;
}
return false;
}
};func searchMatrix(matrix [][]int, target int) bool {
m, n := len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
for i, j := m-1, 0; i >= 0 && j < n; {
if matrix[i][j] == target {
return true
}
if matrix[i][j] > target {
i--
} else {
j++
}
}
return false
}use std::cmp::Ordering;
impl Solution {
pub fn search_matrix(matrix: Vec<Vec<i32>>, target: i32) -> bool {
let m = matrix.len();
let n = matrix[0].len();
let mut left = 0;
let mut right = m * n;
while left < right {
let mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
let i = mid / n;
let j = mid % n;
match matrix[i][j].cmp(&target) {
Ordering::Equal => {
return true;
}
Ordering::Less => {
left = mid + 1;
}
Ordering::Greater => {
right = mid;
}
}
}
false
}
}/**
* @param {number[][]} matrix
* @param {number} target
* @return {boolean}
*/
var searchMatrix = function (matrix, target) {
const m = matrix.length,
n = matrix[0].length;
for (let i = m - 1, j = 0; i >= 0 && j < n; ) {
if (matrix[i][j] == target) {
return true;
}
if (matrix[i][j] > target) {
--i;
} else {
++j;
}
}
return false;
};