| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
|
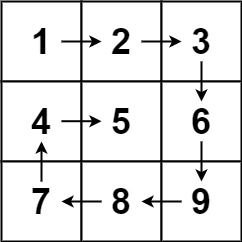
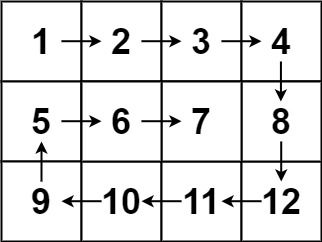
Given an m x n matrix, return all elements of the matrix in spiral order.
Example 1:
Input: matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]] Output: [1,2,3,6,9,8,7,4,5]
Example 2:
Input: matrix = [[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8],[9,10,11,12]] Output: [1,2,3,4,8,12,11,10,9,5,6,7]
Constraints:
m == matrix.lengthn == matrix[i].length1 <= m, n <= 10-100 <= matrix[i][j] <= 100
We can simulate the entire traversal process. We use
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def spiralOrder(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
m, n = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
dirs = (0, 1, 0, -1, 0)
vis = [[False] * n for _ in range(m)]
i = j = k = 0
ans = []
for _ in range(m * n):
ans.append(matrix[i][j])
vis[i][j] = True
x, y = i + dirs[k], j + dirs[k + 1]
if x < 0 or x >= m or y < 0 or y >= n or vis[x][y]:
k = (k + 1) % 4
i += dirs[k]
j += dirs[k + 1]
return ansclass Solution {
public List<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
int[] dirs = {0, 1, 0, -1, 0};
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
boolean[][] vis = new boolean[m][n];
for (int h = m * n; h > 0; --h) {
ans.add(matrix[i][j]);
vis[i][j] = true;
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x < 0 || x >= m || y < 0 || y >= n || vis[x][y]) {
k = (k + 1) % 4;
}
i += dirs[k];
j += dirs[k + 1];
}
return ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<int> spiralOrder(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size();
int dirs[5] = {0, 1, 0, -1, 0};
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
vector<int> ans;
bool vis[m][n];
memset(vis, false, sizeof(vis));
for (int h = m * n; h; --h) {
ans.push_back(matrix[i][j]);
vis[i][j] = true;
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x < 0 || x >= m || y < 0 || y >= n || vis[x][y]) {
k = (k + 1) % 4;
}
i += dirs[k];
j += dirs[k + 1];
}
return ans;
}
};func spiralOrder(matrix [][]int) (ans []int) {
m, n := len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
vis := make([][]bool, m)
for i := range vis {
vis[i] = make([]bool, n)
}
dirs := [5]int{0, 1, 0, -1, 0}
i, j, k := 0, 0, 0
for h := m * n; h > 0; h-- {
ans = append(ans, matrix[i][j])
vis[i][j] = true
x, y := i+dirs[k], j+dirs[k+1]
if x < 0 || x >= m || y < 0 || y >= n || vis[x][y] {
k = (k + 1) % 4
}
i, j = i+dirs[k], j+dirs[k+1]
}
return
}function spiralOrder(matrix: number[][]): number[] {
const m = matrix.length;
const n = matrix[0].length;
const ans: number[] = [];
const vis: boolean[][] = Array.from({ length: m }, () => Array(n).fill(false));
const dirs = [0, 1, 0, -1, 0];
for (let h = m * n, i = 0, j = 0, k = 0; h > 0; --h) {
ans.push(matrix[i][j]);
vis[i][j] = true;
const x = i + dirs[k];
const y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x < 0 || x >= m || y < 0 || y >= n || vis[x][y]) {
k = (k + 1) % 4;
}
i += dirs[k];
j += dirs[k + 1];
}
return ans;
}impl Solution {
pub fn spiral_order(matrix: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<i32> {
let m = matrix.len();
let n = matrix[0].len();
let mut dirs = vec![0, 1, 0, -1, 0];
let mut vis = vec![vec![false; n]; m];
let mut i = 0;
let mut j = 0;
let mut k = 0;
let mut ans = Vec::new();
for _ in 0..(m * n) {
ans.push(matrix[i][j]);
vis[i][j] = true;
let x = i as i32 + dirs[k] as i32;
let y = j as i32 + dirs[k + 1] as i32;
if x < 0 || x >= m as i32 || y < 0 || y >= n as i32 || vis[x as usize][y as usize] {
k = (k + 1) % 4;
}
i = (i as i32 + dirs[k] as i32) as usize;
j = (j as i32 + dirs[k + 1] as i32) as usize;
}
ans
}
}/**
* @param {number[][]} matrix
* @return {number[]}
*/
var spiralOrder = function (matrix) {
const m = matrix.length;
const n = matrix[0].length;
const ans = [];
const vis = Array.from({ length: m }, () => Array(n).fill(false));
const dirs = [0, 1, 0, -1, 0];
for (let h = m * n, i = 0, j = 0, k = 0; h > 0; --h) {
ans.push(matrix[i][j]);
vis[i][j] = true;
const x = i + dirs[k];
const y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x < 0 || x >= m || y < 0 || y >= n || vis[x][y]) {
k = (k + 1) % 4;
}
i += dirs[k];
j += dirs[k + 1];
}
return ans;
};public class Solution {
public IList<int> SpiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
int m = matrix.Length, n = matrix[0].Length;
int[] dirs = { 0, 1, 0, -1, 0 };
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
IList<int> ans = new List<int>();
bool[,] vis = new bool[m, n];
for (int h = m * n; h > 0; --h) {
ans.Add(matrix[i][j]);
vis[i, j] = true;
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x < 0 || x >= m || y < 0 || y >= n || vis[x, y]) {
k = (k + 1) % 4;
}
i += dirs[k];
j += dirs[k + 1];
}
return ans;
}
}Notice that the range of matrix element values is
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def spiralOrder(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
m, n = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
dirs = (0, 1, 0, -1, 0)
i = j = k = 0
ans = []
for _ in range(m * n):
ans.append(matrix[i][j])
matrix[i][j] += 300
x, y = i + dirs[k], j + dirs[k + 1]
if x < 0 or x >= m or y < 0 or y >= n or matrix[x][y] > 100:
k = (k + 1) % 4
i += dirs[k]
j += dirs[k + 1]
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
matrix[i][j] -= 300
return ansclass Solution {
public List<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
int[] dirs = {0, 1, 0, -1, 0};
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (int h = m * n; h > 0; --h) {
ans.add(matrix[i][j]);
matrix[i][j] += 300;
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x < 0 || x >= m || y < 0 || y >= n || matrix[x][y] > 100) {
k = (k + 1) % 4;
}
i += dirs[k];
j += dirs[k + 1];
}
for (i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
matrix[i][j] -= 300;
}
}
return ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<int> spiralOrder(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size();
int dirs[5] = {0, 1, 0, -1, 0};
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
vector<int> ans;
for (int h = m * n; h; --h) {
ans.push_back(matrix[i][j]);
matrix[i][j] += 300;
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x < 0 || x >= m || y < 0 || y >= n || matrix[x][y] > 100) {
k = (k + 1) % 4;
}
i += dirs[k];
j += dirs[k + 1];
}
for (i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
matrix[i][j] -= 300;
}
}
return ans;
}
};func spiralOrder(matrix [][]int) (ans []int) {
m, n := len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
dirs := [5]int{0, 1, 0, -1, 0}
i, j, k := 0, 0, 0
for h := m * n; h > 0; h-- {
ans = append(ans, matrix[i][j])
matrix[i][j] += 300
x, y := i+dirs[k], j+dirs[k+1]
if x < 0 || x >= m || y < 0 || y >= n || matrix[x][y] > 100 {
k = (k + 1) % 4
}
i, j = i+dirs[k], j+dirs[k+1]
}
for i = 0; i < m; i++ {
for j = 0; j < n; j++ {
matrix[i][j] -= 300
}
}
return
}function spiralOrder(matrix: number[][]): number[] {
const m = matrix.length;
const n = matrix[0].length;
const ans: number[] = [];
const dirs = [0, 1, 0, -1, 0];
for (let h = m * n, i = 0, j = 0, k = 0; h > 0; --h) {
ans.push(matrix[i][j]);
matrix[i][j] += 300;
const x = i + dirs[k];
const y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x < 0 || x >= m || y < 0 || y >= n || matrix[x][y] > 100) {
k = (k + 1) % 4;
}
i += dirs[k];
j += dirs[k + 1];
}
for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
matrix[i][j] -= 300;
}
}
return ans;
}impl Solution {
pub fn spiral_order(mut matrix: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<i32> {
let m = matrix.len();
let n = matrix[0].len();
let mut dirs = vec![0, 1, 0, -1, 0];
let mut i = 0;
let mut j = 0;
let mut k = 0;
let mut ans = Vec::new();
for _ in 0..(m * n) {
ans.push(matrix[i][j]);
matrix[i][j] += 300;
let x = i as i32 + dirs[k] as i32;
let y = j as i32 + dirs[k + 1] as i32;
if x < 0
|| x >= m as i32
|| y < 0
|| y >= n as i32
|| matrix[x as usize][y as usize] > 100
{
k = (k + 1) % 4;
}
i = (i as i32 + dirs[k] as i32) as usize;
j = (j as i32 + dirs[k + 1] as i32) as usize;
}
for i in 0..m {
for j in 0..n {
matrix[i][j] -= 300;
}
}
ans
}
}/**
* @param {number[][]} matrix
* @return {number[]}
*/
var spiralOrder = function (matrix) {
const m = matrix.length;
const n = matrix[0].length;
const ans = [];
const dirs = [0, 1, 0, -1, 0];
for (let h = m * n, i = 0, j = 0, k = 0; h > 0; --h) {
ans.push(matrix[i][j]);
matrix[i][j] += 300;
const x = i + dirs[k];
const y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x < 0 || x >= m || y < 0 || y >= n || matrix[x][y] > 100) {
k = (k + 1) % 4;
}
i += dirs[k];
j += dirs[k + 1];
}
for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
matrix[i][j] -= 300;
}
}
return ans;
};public class Solution {
public IList<int> SpiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
int m = matrix.Length, n = matrix[0].Length;
int[] dirs = { 0, 1, 0, -1, 0 };
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
IList<int> ans = new List<int>();
for (int h = m * n; h > 0; --h) {
ans.Add(matrix[i][j]);
matrix[i][j] += 300;
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x < 0 || x >= m || y < 0 || y >= n || matrix[x][y] > 100) {
k = (k + 1) % 4;
}
i += dirs[k];
j += dirs[k + 1];
}
for (int a = 0; a < m; ++a) {
for (int b = 0; b < n; ++b) {
matrix[a][b] -= 300;
}
}
return ans;
}
}